 For this study, 20 lung cancer patients underwent exhale/inhale breath hold CT (BHCT), free-breathing four-dimensional CT (4DCT) and Galligas PET ventilation scans in a single session on a combined 4DPET/CT scanner. The purpose of the study was to enable comparisons between: (i) CT ventilation images derived from exhale/inhale BHCT scans, (ii) CT ventilation images derived from free-breathing 4DCT scans, and (iii) Galligas PET (nuclear medicine) ventilation scans. This dataset can build the international capacity for prototyping and evaluating new CT ventilation imaging technologies.
All image acquisitions were performed on a Siemens Biograph mCT.S/64 PET/CT scanner (Siemens, Knoxville, USA) at the Royal North Shore Hospital between 2013 and 2015. A total of 20 4DCT scans, 20 inhale/exhale BHCT scans, 20 Galligas PET scans and 19 attenuation CT scans (missing for CT-PET-VI-07) were successfully acquired for the 20 patients and included in this dataset. Real World Value Mapping files generated with the PET scans have been included. This DICOM file type is normally used to convert activity to estimated tissue uptake Standardized Uptake Values (SUVs) assuming tissue density of 1g/mL. However, for this study radiotracer was not injected intravenously into tissue, but inhaled into the lung where this assumption does not hold, so these files should be used with caution
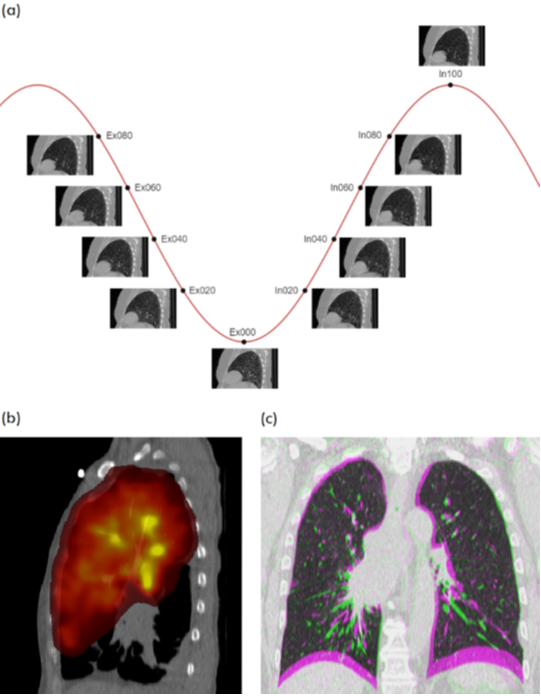
For the exhale/inhale BHCT scans, patients were instructed to hold their breath at approximately 80% of maximum inhalation and exhalation, with Audiovisual Biofeedback used to help guide the breath hold procedure. Settings for the BHCT image acquisitions were: 120 kVp, 120 mAs, 0.8 pitch with a breath-hold time of 10s. The field of view for the CT images was approximately 50 cm from the pharynx to the stomach. Meanwhile the 4DCT scans were acquired with the use of a respiratory motion sensor, the Anzai AZ-733V system (Anzai Medical Co., Tokyo, Japan) for retrospective sorting of CT slices into 10 respiratory phase bins; the exhale and inhale phase bins are provided with the present dataset. 4DCT scans were performed using a helical acquisition and tube settings 120 kVp, 80-200 mA, with 0.5s gantry rotation and 0.09 pitch. The Galligas PET scans (and corresponding attenuation correction CT) were acquired under free-breathing using a standard non-gated protocol. Galligas PET scans were acquired at 2 bed positions of 5 min each, with attenuation correction using a low dose CT (120 kVp; 0.8 pitch, 50 mAs). This study was a prospective single institution clinical trial approved by the health district ethics committee, (HREC/12/169) and registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12612000775819). | 