...
| Excerpt |
|---|
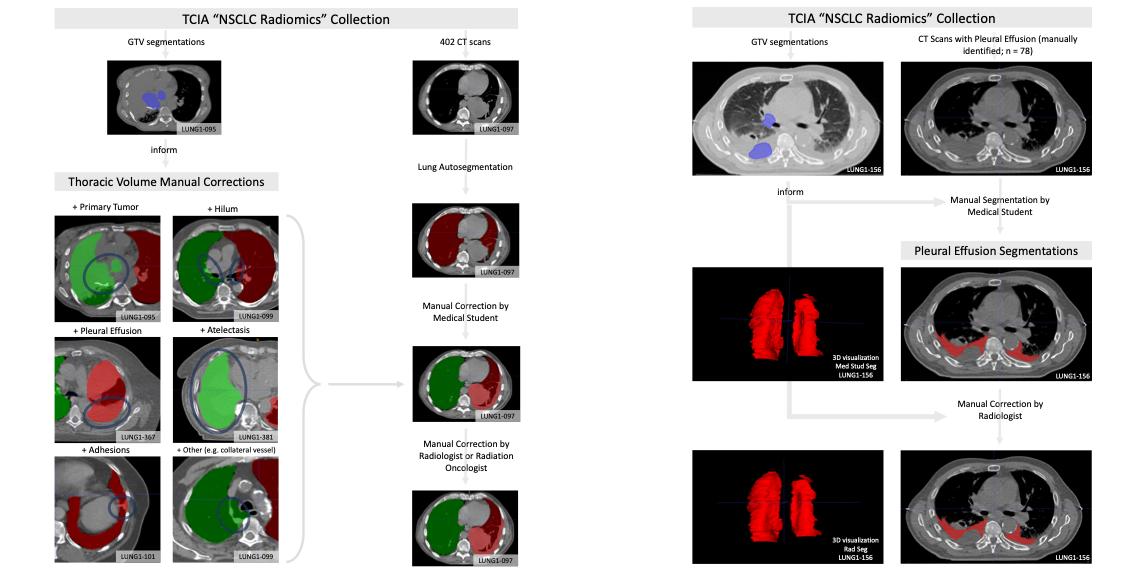
Automated or semi-automated algorithms intended for chest CT analyses typically require the creation of a 3D map of the thoracic volume as their initial step. Identifying this anatomic region precedes fundamental tasks such as lung structure segmentation, lesion detection, and radiomics feature extraction in analysis pipelines. However, automatic approaches to segment the thoracic volume maps struggle to perform consistently in subjects with diseased lungs – yet this is exactly the circumstance for which pipeline analyses would be most useful. To address this need, we have createdPleThora, a dataset of pleural effusion and thoracic cavity segmentations in subjects with diseased lungs. PleThora consists of left and right thoracic cavity segmentations delineated on 402 CT scans from The Cancer Imaging Archive NSCLC Radiomics collection as well as separate segmentations labeling pleural effusions alone. Thoracic cavity segmentations include lung parenchyma, tumor, atelectasis, adhesions, and effusion. PleThora is a tool for medical image preprocessing and segmentation researchers to build and compare approaches for region-of-interest identification and analysis. The thoracic cavity segmentations were generated automatically by a U-Net based algorithm trained on chest CTs without cancer, manually corrected by a medical student, and revised by a radiation oncologist or a radiologist. Pleural effusion segmentations were manually delineated by a medical student and revised by a radiologist. Expert GTV segmentations already provided by the NSCLC Radiomics collection helped inform our segmentations, and areas of the effusion that overlap with GTVs are not included. Researchers interested in discriminating between GTV and effusion using imaging biomarker inputs may find our pleural effusion segmentations useful, especially when paired with the GTV segmentations provided in the NSCLC Radiomics collection. Tabular data are also provided, including GTV, thorax, and effusion volumes (in cm3), tumor location, and image metadata. Additionally, we standardized a train/test split for training deep learning algorithms with the thoracic cavity segmentations. Note: These segmentations use the RPI orientation, but the original DICOM files are oriented using the RAI convention. As a result, some tools such as ITK-SNAP will not render the segmentations in the correct orientation when visualized. The authors of these data suggest using software like Mango (http://ric.uthscsa.edu/mango/) or to convert to DICOM files to Nifti with software like dcm2niix (https://github.com/rordenlab/dcm2niix) to address this issue. |
Acknowledgements
...