Versions Compared
Key
- This line was added.
- This line was removed.
- Formatting was changed.
Summary
| Excerpt |
|---|
Purpose: Expert selected landmark points on clinical image pairs provide a basis for rigid registration validation. Using combinatorial rigid registration optimization (CORRO) we provide a statistically characterized reference data set for image registration of the pelvis by estimating the optimal ground truth. Methods: Landmark points for each CT/CBCT image pair for 58 pelvic cases were identified. From the identified landmark pairs, combination subsets of k-number of landmark pairs were generated without repeat, to form a k-set for k=4, 8, &12. An affine registration between the image pairs was calculated for each k-combination set (2,000-8,000,000). The mean and the standard deviation of the registration were used as the final registration for each image pair. Joint entropy was employed to measure and compare the quality of CORRO to commercially available software. Results: An average of 154 (range: 91-212) landmark pairs were selected for each CT/CBCT image pair. The mean standard deviation of the registration output decreased as the k-size increased for all cases. In general the joint entropy evaluated was found to be lower than results from commercially available software. Of all 58 cases 58.3% of the k=4, 15% of k=8 and 18.3% of k=12 resulted in the better registration using CORRO as compared to 8.3% from a commercial registration software. The minimum joint entropy was determined for one case and found to exist at the estimated registration mean in agreement with the CORRO approach. Conclusion: The results demonstrate that CORRO works even in the extreme case of the pelvic anatomy where the CBCT suffers from reduced quality due to increased noise levels. The estimated ground truth using CORRO was found to be better than commercially available software for all k-sets tested. Additionally, the k-set of 4 resulted in overall best outcomes when compared to k=8 and 12, which is anticipated because k=8 and 12 are more likely to have combinations that affected the accuracy of the registration. |
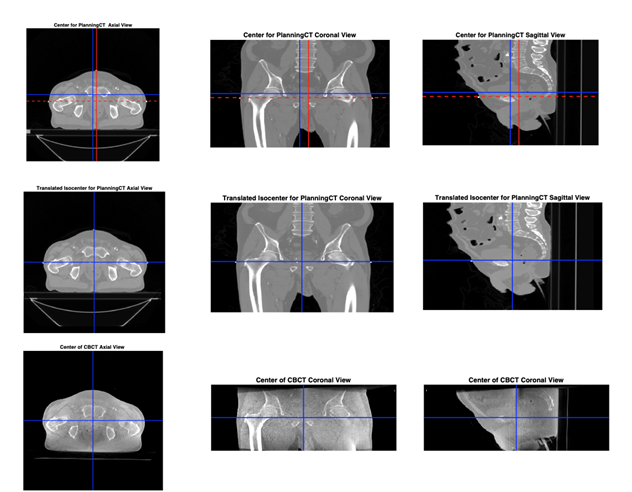
Figure 1. Content of planning CT shifted to the machine isocenter. Top left to right - axial, coronal and sagittal planning CT image with machine isocenter in red and image isocenter in blue. Middle left to right - axial, coronal and sagittal planning CT at machine isocenter. Bottom left to right - axial, coronal and sagittal CBCT at machine isocenter.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the individuals and institutions that have provided data for this collection:
Beaumont Health : Afua Yorke, Gary McDonald, David Solis, Thomas Guerrero. We thank Beaumont Hospital Royal Oak MI, for their support. And thanks to Charles K. Yorke, Ph.D., and Brad J. Roth Ph.D.
| Localtab Group | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

