...
| Excerpt |
|---|
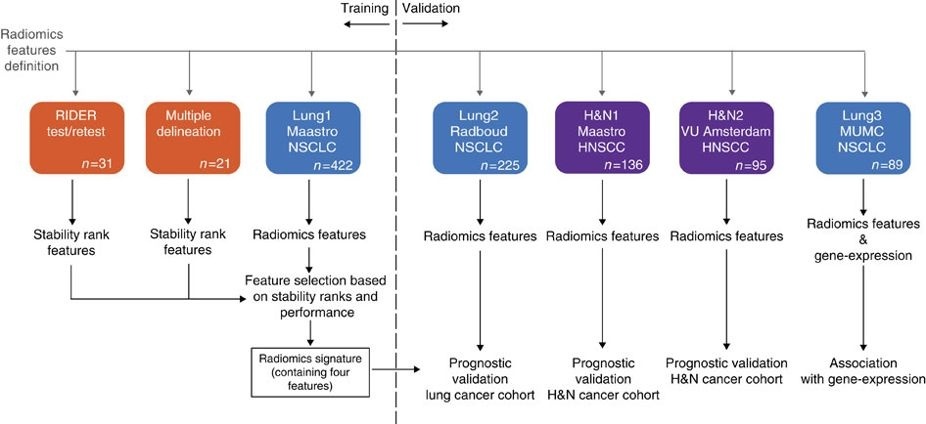
This collection contains clinical data and computed tomography (CT) from 22 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) radiotherapy patients. For 21 of these patients with pre-treatment CT scans, repeated blinded manual delineations by five different radiation oncologists of the 3D volume of the gross tumor volume on CT and clinical outcome data are available. The above was repeated with the same set of five radiation oncologists, using an in-house autosegmentation tool for initial delineation followed by manual adjustment of the gross tumor volume outline. For one patient, clinical data and CT was available but the tumor delineations were not extracted. This patient was included in this collection for the sake of completeness. This dataset refers to the multiple "Multiple delineation" dataset of the study published in Nature Communications (http://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5006). In short, the publication used a radiomics approach to computed tomography data of 1,019 patients with lung or head-and-neck cancer. Radiomics refers to the comprehensive quantification of tumor phenotypes by applying a large number of quantitative image features. In the published analysis, 440 features quantifying tumor image intensity, shape, and texture were extracted. We found that a large number of radiomic features have prognostic power in independent data sets, many of which were not identified as significant before. Radiogenomics analysis revealed that a prognostic radiomic signature, capturing intra-tumor heterogeneity, was associated with underlying gene-expression patterns. These data suggest that radiomics identifies a general prognostic phenotype existing in both lung and head-and-neck cancer. This may have a clinical impact as imaging is routinely used in clinical practice, providing an unprecedented opportunity to improve decision-support in cancer treatment at low cost. This dataset is intended to be open access to support repeatability and reproducibility of research in the radiomics domain. This dataset will be the subject of an upcoming Nature Data article addressing FAIR radiomics practices to support transparency, harmonization and collaboration on radiomics. |
...