Summary
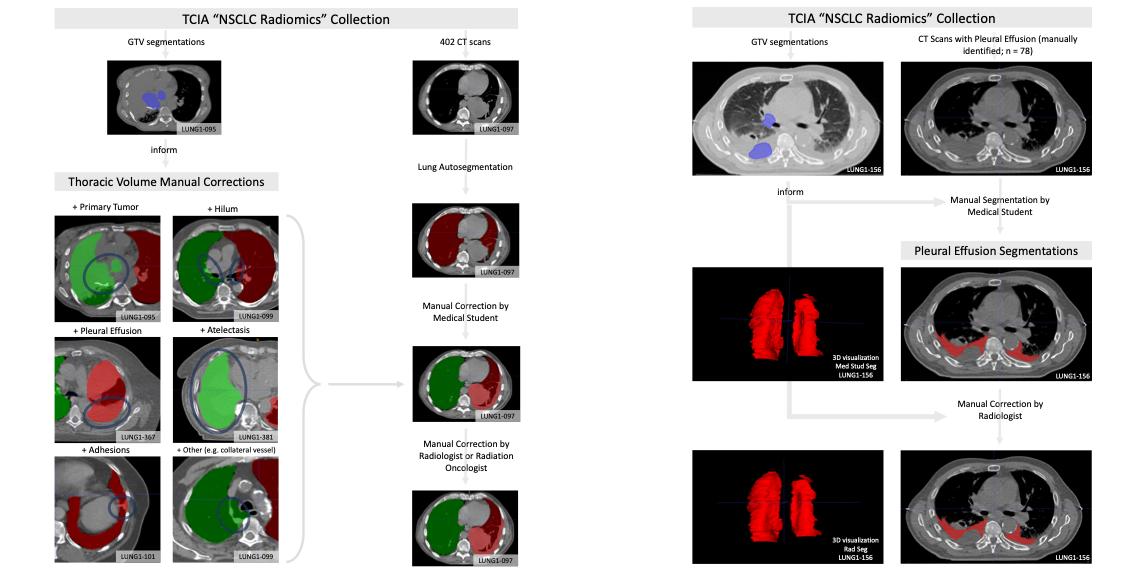
Automated or semi-automated algorithms intended for chest CT analyses typically require the creation of a 3D map of the thoracic volume as their initial step. Identifying this anatomic region precedes fundamental tasks such as lung structure segmentation, lesion detection, and radiomics feature extraction in analysis pipelines. However, automatic approaches to segment the thoracic volume maps struggle to perform consistently in subjects with diseased lungs, yet this is exactly the circumstance for which pipeline analyses would be most useful. To address this need, we have created a dataset of thoracic volume segmentations on subjects with diseased lungs. These will help the research community compare and contrast their approaches for this foundational processing step on clinically relevant data.This dataset consists of left and right thoracic volume segmentations delineated on 402 CT scans from The Cancer Imaging Archive NSCLC Radiomics collection. Thoracic segmentations include lung parenchyma, tumor, atelectasis, and effusion when present. On scans where effusion is present, separate segmentations labeling pleural effusion alone are also provided.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the individuals and institutions that have provided data for this collection:
- University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA - Special thanks to Kendall Kiser, MS Biomedical Informatics, from the Department of Radiation Oncology.
- The University of Texas Health Science Center School of Biomedical Informatics, Houston, TX, USA
- John P. and Kathrine G. McGovern Medical School, Houston, TX. Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging.
Data Access
Click the Download button to save the data.
| Data Type | Download all or Query/Filter |
|---|---|
Images (NIfTI, 23.6 GB) zip Thoracic Segmentations | |
Images (NIfTI, 4.9 GB) zip Pleural Effusion Segmentations | |
Thorax and Pleural Effusion Segmentation Metadata (CSV) |
Click the Versions tab for more info about data releases.
Detailed Description
Table will be populated once all data received. Any additional data description will be added here.
This dataset consists of left and right thoracic volume segmentations delineated on 402 CT scans from The Cancer Imaging Archive NSCLC Radiomics collection. Thoracic segmentations include lung parenchyma, tumor, atelectasis, adhesions, and effusion, when present. The initial thoracic segmentations were first generated automatically by a U-Net based algorithm trained on chest CTs without cancer, manually corrected by a medical student, and revised by a radiation oncologist or a radiologist.
On scans where effusion is present, separate segmentations labeling pleural effusion alone are also provided. Pleural effusion segmentations were manually delineated by a medical student and revised by a radiologist. Expert GTV segmentations already provided by the NSCLC Radiomics collection helped inform our segmentations, and areas of the effusion that overlap with GTVs are not included. Researchers interested in discriminating between GTV and effusion using imaging biomarker inputs may find our pleural effusion segmentations useful, especially when paired with the GTV segmentations provided in the NSCLC Radiomics collection.
Tabular data extending the tabular data accompanying the NSCLC Radiomics collection are also provided, including GTV, thorax, and effusion volumes (in cm3), tumor location, and image metadata. This dataset was utilized in a clinical informatics study correlating autosegmentation accuracy as gauged by several common metrics with time required for manual corrections.
Citations & Data Usage Policy
These collections are freely available to browse, download, and use for commercial, scientific and educational purposes as outlined in the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Questions may be directed to help@cancerimagingarchive.net. Please be sure to acknowledge both this data set and TCIA in publications by including the following citations in your work:
Data Citation
Kiser, K.J., Ahmed, S. M. E. H., Stieb, S.M., Mohamed, A.S.R., Elhalawani, H., Park, P.Y.S., Doyle, N.S., Wang, B.J., Barman, A., Fuller, C.D., Giancardo, L. (2020). Data from the Thoracic volume and pleural effusion segmentations in diseased lungs for benchmarking chest CT processing pipelines [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/tcia.2020.6c7y-gq39.
Grant Citations
- Swiss Cancer League (BIL KLS-4300-08-2017).
- Learning Healthcare Award funded by the UTHealth Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS).
- NIH grant UL1TR003167.
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Institute for Dental and Craniofacial Research Establishing Outcome Measures Award (1R01DE025248/R56DE025248) and an Academic Industrial Partnership Grant (R01DE028290)
National Cancer Institute (NCI) Early Phase Clinical Trials in Imaging and Image-Guided Interventions Program (1R01CA218148)
NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) Pilot Research Program Award from the UT MD Anderson CCSG Radiation Oncology and Cancer Imaging Program (P30CA016672)
NIH/NCI Head and Neck Specialized Programs of Research Excellence (SPORE) Developmental Research Program Award (P50 CA097007)
National Science Foundation (NSF), Division of Mathematical Sciences, Joint NIH/NSF Initiative on Quantitative Approaches to Biomedical Big Data (QuBBD) Grant (NSF 1557679)
NSF Division of Civil, Mechanical, and Manufacturing Innovation (CMMI) standard grant (NSF 1933369) a National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) Research Education Programs for Residents and Clinical Fellows Grant (R25EB025787-01)
NIH Big Data to Knowledge (BD2K) Program of the NCI Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science Award (1R01CA214825).
Direct infrastructure support was provided by the multidisciplinary Stiefel Oropharyngeal Research Fund of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Charles and Daneen Stiefel Center for Head and Neck Cancer and the Cancer Center Support Grant (P30CA016672) and the MD Anderson Program in Image-guided Cancer Therapy.
Direct industry grant support, honoraria, and travel funding from Elekta AB
TCIA Citation
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M, Tarbox L, Prior F. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository, Journal of Digital Imaging, Volume 26, Number 6, December, 2013, pp 1045-1057. DOI: 10.1007/s10278-013-9622-7
Data Citation
Aerts, H. J. W. L., Wee, L., Rios Velazquez, E., Leijenaar, R. T. H., Parmar, C., Grossmann, P., … Lambin, P. (2019). Data From NSCLC-Radiomics [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2015.PF0M9REI
Other Publications Using This Data
TCIA maintains a list of publications which leverage TCIA data. If you have a manuscript you'd like to add please contact the TCIA Helpdesk.