- Created by Tracy Nolan, last modified by Pam Angelus on Mar 19, 2020
You are viewing an old version of this page. View the current version.
Compare with Current View Page History
« Previous Version 43 Next »
Summary
There currently is a dearth of phantom scans on large samples. This data collection contains one physical phantom, imaged across three protocols, on 100 scanners. This provides population data that can be used to quantify inter-scanner variability. This data can be used to determine how robust specific radiomics or other quantitative imaging signatures are.
Protocol
Computed tomography scans were acquired on 100 scanners at 35 clinics: 51 GE scanners, 20 Philips scanners, 11 Toshiba scanners, and 1 Philips and Neusoft Medical System scanner. The commonly used chest and head protocols of the local clinic were acquired without changing the protocol parameters. Additionally, a controlled protocol was acquired that was designed to minimize radiomics feature differences between manufacturers. The settings for the controlled protocol were: tube voltage, 120 kV(p); tube current, 200 mA∙s; helical scan type; spiral pitch factor, 1.0; 50-cm display field of view; and image thickness, 3 mm (except for GE scanners, which used an image thickness of 2.5 mm). The convolution kernel was standard for GE; C for Philips; B31f, B31s for Siemens; and FC08 for Toshiba. However, the kernel used for the Toshiba scans switched from FC18 (six scanners) to FC08 (five scanners) halfway through owing to a study by Mackin et al. (Medical Physics, 2018) that found the FC08 kernel to match the GE standard kernel best. K-means clustering showed that the scanners did not cluster by kernel type, thus all Toshiba scanners were included.
There were 94 scanners that had a controlled protocol scan that could be used: 48 GE, 18 Philips, 17 Siemens, and 11 Toshiba scanners; 93 scanners that had a local chest protocol scan that could be used: 47 GE, 19 Philips, 17 Siemens, and 10 Toshiba scanners; and 88 scanners that had a local head protocol scan that could be used: 46 GE, 18 Philips, 14 Siemens, and 10 Toshiba scanners. The various reasons that scans could not be used were as follows: the field of view did not encompass all the cartridges, the scan extent did not cover the length of the phantom, and the scan was acquired with variable image thickness.
Acknowledgements
This data set was provided to TCIA by Rachel Ger, Shouhao Zhou, Pai-Chun Chi, Hannah Lee, Rick Layman, Kyle Jones, David Goff, Carlos Cardenas, Clifton Fuller, Rebecca Howell, Heng Li, Jason Stafford, Laurence Court, Dennis Mackin.
Data Access
Click the Download button to save a ".tcia" manifest file to your computer, which you must open with the NBIA Data Retriever. Click the Search button to open our Data Portal, where you can browse the data collection and/or download a subset of its contents.
| Data Type | Download all or Query/Filter |
|---|---|
| Images (DICOM, 13.4GB) | |
Acquisition & reconstruction settings (note: Acquisition and reconstruction settings within the DICOM header may be incorrect. The settings used for each scan are provided in the attached spreadsheet. |
Click the Versions tab for more info about data releases.
Detailed Description
Collection Statistics | Updated |
|---|---|
Modalities | RT STRUCT, CT |
Number of Patients | 95 |
Number of Studies | 113 |
Number of Series | 550 |
Number of Images | 25,612 |
| Image Size (GB) | 13.4 |
Citations & Data Usage Policy
This collection is freely available to browse, download, and use for commercial, scientific and educational purposes as outlined in the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. See TCIA's Data Usage Policies and Restrictions for additional details. Questions may be directed to help@cancerimagingarchive.net.
Please be sure to include the following citations in your work if you use this data set:
Data Citation
Ger R, Zhou S, Chi P-C, Lee H, Layman R, Jones K, Goff DL, Fuller CD, Howell RM, Heng L, Stafford RJ, Court LE, Mackin D. (2019). Data from CT Phantom Scans for Head, Chest, and Controlled Protocols on 100 Scanners (CC-Radiomics-Phantom-3) [Data set]. The Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/tcia.2019.j71i4fah
Manuscript Citation
Ger, Rachel B.; Zhou, Shouhao; Chi, Pai-Chun Melinda; Lee, Hannah J.; Layman, Rick R.; Jones, A. Kyle; Goff, David L.; Fuller, Clifton D.; Howell, Rebecca M.; Li, Heng; Stafford, R. Jason; Court, Laurence E.; Mackin, Dennis S. (2018) Comprehensive Investigation on Controlling for CT Imaging Variabilities in Radiomics Studies. Scientific Reports 8:13047. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-31509-z
TCIA Citation
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P, Moore S, Phillips S, Maffitt D, Pringle M, Tarbox L, Prior F. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository, Journal of Digital Imaging, Volume 26, Number 6, December, 2013, pp 1045-1057. DOI: 10.1007/s10278-013-9622-7
Other Publications Using This Data
TCIA maintains a list of publications which leverage our data. If you have a publication you'd like to add please contact the TCIA Helpdesk.
Version 1 (Current): Updated
| Data Type | Download all or Query/Filter |
|---|---|
| Images (DICOM, 13.4 GB) | (Requires NBIA Data Retriever.) |
| Acquisition & reconstruction settings (XLSX, 29kB) |
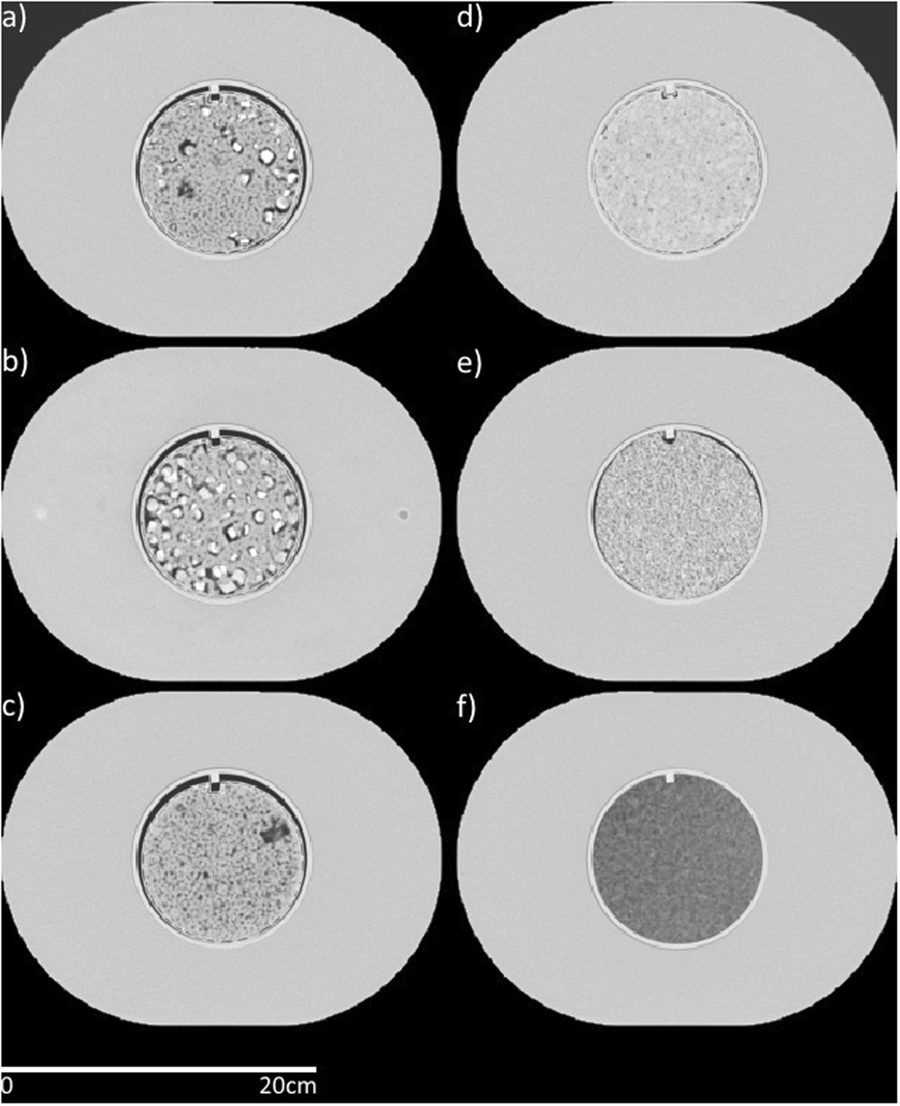
Axial views from a computed tomography scan of the radiomics phantom used. The cartridges are (a) 50% acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), 25% acrylic beads, and 25% polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pieces (percentages are by weight), (b) 50% ABS and 50% PVC pieces, (c) 50% ABS and 50% acrylic beads, (d) hemp seeds in polyurethane, (e) shredded rubber, and (f) dense cork.
The high-density polystyrene buildup is seen outside the cartridges with dimensions of 28cm×21cm×22cm. The cartridges had a diameter of 10.8 cm. Window width: 1600, window level: -300.
- No labels