When data is submitted to TCIA it undergoes an extensive curation process to assure completeness, proper formatting to facilitate discovery and data reuse and removal of all protected health information. Once data is released on the public TCIA repository it is Published to the world. This publication is associated with the creation of a Digital Object Identifier that allows direct access to the data.
In addition to data publication via TCIA we strongly urge researchers who submit data to TCIA to also submit a Data Descriptor publication to a journal such as Nature Scientific Data. In this type of publication the authors will describe the data acquisition process, the experiment that drove this data collection and value of the data for future research (see each journal for specific content requirements). A Data Descriptor is a scientific paper that includes the DOI to the data previously published on TCIA and helps to call the attention of the scientific community to the data you have submitted. The details provided in a Data Descriptor publication greatly enhance the value of your contribution.
A Data Descriptor is different from a scholarly paper in which you describe your experiment and present the results of your analysis. Many journals do not provide sufficient space for details of data acquisition. So today you can provide those details and the data you collected by making full use of TCIA and journals that support data publication. In summary we urge you to:
- Submit your data to TCIA for publication.
- Submit a Data Descriptor article including the TCIA provided DOI to describe your data and how it was acquired.
- Submit a paper describing your experiment and results.
Please remember in all of your publications based on TCIA data to include appropriate references to TCIA so we can identify your publications, reference them, and make them easily available to other researchers from the TCIA web site. These citations are critical for providing continued justification of funding from the agencies that support TCIA, and are what allow us to provide this data to you free of charge. Guidelines for how to cite TCIA can be found on our Citation Guidelines wiki page. In addition we would like to list these publications here on our web site. If you have utilized TCIA in your research please contact us at help@cancerimagingarchive.net so that we can include your publications in the list below. The publication list below includes references to the original data collection as well as publications that specifically used data from TCIA.
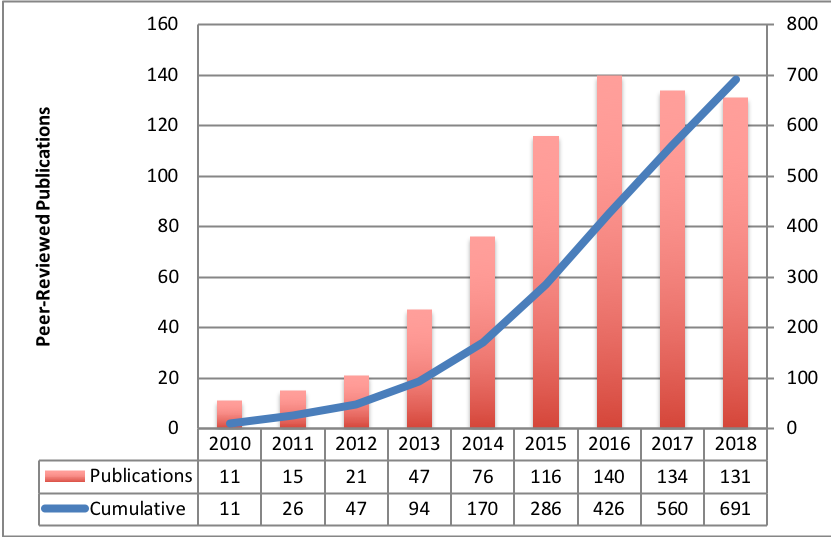
A listing of published analysis results data sets based upon TCIA-hosted data is provided here.
Download citation list (Endnote XML format)
For convenience you can also obtain the publications specifically based on TCIA in Endnote XML format: Pubs_basedon_TCIA_1218.xml. This should be usable as input to your favorite reference management system.
TCIA-Related Publication History
Table of Contents
TCIA General
- Li, H., & Mueller, K. (2017). Low-dose CT streak artifacts removal using deep residual neural network. Fully 3D Image Reconstruction in Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. Xi'an: Stony Brook University. (link)
Vidya, K., & Kurian, M. (2018). Novel framework for breast cancer classification for retaining computational efficiency and precise diagnosis. Communications Applied Electronics, 7(15), 1-6. (link)
Brassey, C. A., O'Mahoney, T. G., Chamberlain, A. T., & Sellers, W. I. (2017). A volumetric technique for fossil body mass estimation applied to Australopithecus afarensis. Journal of Human Evolution, 115, 47-64. DOI:10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.07.014
Omotosho, A., Oluwatobi, A. E., Oluwaseun, O. R., Chukwuka, A. E., & Adekanmi, A. (2018). A neuro-fuzzy based system for the classification of cells as cancerous or non-cancerous. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 7(5), 155-166. Retrieved from http://www.ijmrhs.com/medical-research/a-neurofuzzy-based-system-for-the-classification-of-cells-as-cancerous-or-noncancerous.pdf
Russell, P., Fountain, K., Wolverton, D., & Ghosh, D. (2018). TCIA pathfinder: An R client for The Cancer Imaging Archive REST API. Cancer Research. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0678
Bennett, W., Smith, K., Jarosz, Q., Nolan, T., & Bosch, W. (2018). Reengineering workflow for curation of DICOM datasets. Journal of Digital Imaging, 1-9. DOI:10.1007/s10278-018-0097-4
Yassine, A.-A., Kingsford, W., Xu, Y., Cassidy, J., Lilge, L., & Betz, V. (2018). Automatic interstitial photodynamic therapy planning via convex optimization. Biomedical Optics Express, 9(2), 898-920. DOI:10.1364/BOE.9.000898
- Sharma, M., Bhatt, J. S., & Joshi, M. V. (2018). Early detection of lung cancer from CT images: Nodule segmentation and classification using deep learning. Tenth International Conference on Machine Vision. 106960W. Vienna: SPIE. DOI:10.1117/12.2309530
- Saad, M., & Choi, T.-S. (2018). Computer-assisted subtyping and prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer patients with unresectable tumor. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 67, 1-8. DOI:10.1016/j.compmedimag.2018.04.003
- Nishio, M., Nishizawa, M., Sugiyama, O., Kojima, R., Yakami, M., Kuroda, T., Togashi, K. (2018). Computer aided diagnosis of lung nodule using gradient tree boosting and Bayesian optimization. Plos One, 13(4). DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0195875
- Jenuwine, N. M., Mahesh, S. N., Furst, J. D., & Raicu, D. S. (2018). Lung nodule detection from CT scans using 3D convolutional neural networks without candidate selection. Medical Imaging 2018. 1057539. Houston: SPIE. DOI:10.1117/12.2293918
- Gibson, E., Giganti, F., Hu, Y., Bonmati, E., Bandula, S., Gurusamy, K., Davidson, B., Pereira, S. P., Clarkson, M. J., Barratt, D. C. (2018). Automatic multi-organ segmentation on abdominal CT with dense v-networks. IEEE Transaction on Medical Imaging. DOI:10.1109/TMI.2018.2806309
- Edwards, S., Brown, S., & Lee, M. (2018). Automated 3-D tissue segmentation via clustering. Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Imaging, 5(2). DOI:10.14738/jbemi.52.4204
- Chacko, L. J., Schmidbauer, D. T., Handschuh, S., Reka, A., Fritscher, K. D., Raudaschl, P., Saba, R., Handler, M., Schier, P. P., Baumgarten, D., Fischer, N., Pechriggl, E. J., Brenner, E., Hoermann, R., Glueckert, R., Schrott-Fischer, A. (2018). Analysis of vestibular labyrinthine geometry and variation in the human temporal bone. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12. DOI:10.3389/fnins.2018.00107
- Causey, J., Zhang, J., Ma, S., Jiang, B., Qualls, J., Politte, D. G., Prior, F., Zhang, S., Huang, X. (2018). Highly accurate model for prediciton of lung nodule malignancy with CT scans. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1802/1802.01756.pdf
- Gillmann, C., Arbelaez, P., Penaloza, J. T., Hagen, H., & Wischgoll, T. (2017). Intuitive error space exploration of medical image data in clinical daily routine. Eurographics Conference on Visualization (EuroVis) 2017. DOI:10.2312/eurovisshort.20171148
- Jinu, J., Rajesh, K. R., Pournami, S. C., & Vidya, P. (2017). Interactive 3D Virtual Colonoscopic Navigation For Polyp Detection From CT Images. Procedia Computer Science, 115, 407-414. DOI:10.1016/j.procs.2017.09.099
- Ghosh, D., & Bandyopadhyay, S. K. (2017). Brain tumor detection from MRI image: An approach. International Journal of Applied Research, 3(6), 1152-1159. Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/1916/f00997b627213b46c874a9a133ee8b6fa92e.pdf
- Vallières, M., Laberge, S., Diamant, A., & El Naqa, I. (2017). Enhancement of multimodality texture-based prediction models via optimization of PET and MR image acquisition protocols: a proof of concept. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 62(22), 8536-8565.
- Mitra, S., Banerjee, S., & Hayashi, Y. (2017). Volumetric brain tumour detection from MRI using visual saliency. (J. Najbauer, Ed.) PLOS One, 12(11). 10.1371/journal.pone.0187209
Gueziri, H.-E. (2017). User-centered design and evaluation of interactive segmentation methods for medical images. Montreal: École de technologie supérieure du Quebec. Retrieved from http://espace.etsmtl.ca/1959/2/GUEZIRI_Houssem-Eddine-web.pdf
Lan, R., Zhong, S., Liu, Z., Shi, Z., & Luo, X. (2017). A simple texture feature for retrieval of medical images. Multimedia Tools and Applications. DOI:10.1007/s11042-017-5341-2
Prior, F., Smith, K., Sharma, A., Kirby, J., Tarbox, L., Clark, K., Bennett, W., Nolan, T., Freymann, J. (2017). The public cancer radiology imaging collections of The Cancer Imaging Archive. Nature Scientific Data, 4; 1-7. DOI:10.1038/sdata.2017.124
Kohli, M., Morrison, J. J., Wawira, J., Morgan, M. B., & Hostetter, J., Genereaux, B., Hussain, M., Langer S. G. (2017). Creation and curation of the society of imaging informatics in medicine hackathon dataset. Journal of Digital Imaging, 1-4. DOI:10.1007/s10278-017-0003-5
- Williamson, J.F., Das, S.K., Goodsitt, M.S., Deasy, J.O. (2017). Introducing the Medical Physics Dataset Article. Med. Phys. 44(2); 349-350. DOI:10.1002/mp.12003
- Nida, N; Khan, M. (2016). Efficient Colorization of Medical Imaging based on Colour Transfer Method. U.G. Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: B. Life and Environmental Sciences, 53(4); 253-261. (link)
- Kalpathy-Cramer, J., Zhao, B., Goldgof, D., Gu, Y., Wang, X., Yang, H., Tan, Y., Gillies, R., Napel, S. (2016). A Comparison of Lung Nodule Segmentation Algorithms: Methods and Results from a Multi-institutional Study. J Digit Imaging29(4):476-487. DOI:10.1007/s10278-016-9859-z
Parks, C.L., Monson, K.L. (2016). Automated Facial Recognition of Computed Tomography-Derived Facial Images: Patient Privacy Implications. Journal of Digital Imaging. 1-11. DOI:10.1007/s10278-016-9932-7
Huang, B.E., Mulyasasmita, W., Rajagopal, G. (2016). The Path from Big Data to Precision Medicine.Expert Review of Precision Medicine and Drug Development,1(2):129-143. (link)
- Chatellier, G., Varlet, V., Blachier-Poisson, C. (2016). "Big data" and "open data": What kind of access should researchers enjoy?Therapie. 71(1); 97-105, 107-114.(link)
- Benedict, S.H., Hoffman K., Martel, M.K., Abernethy, A.P., Asher, A.L., Capala, J., Chen, R.C., Chera, B., Couch, J., Deye, J., Efstathiou, J.A., Ford, E., Fraass, B.A., Gabriel, P.E., Huser, V., Kavanagh, B.D., Khuntia, D., Marks, L.B., Mayo, C., McNutt, T., Miller, R.S., Moore, K.L., Prior, F., Roelofs, E., Rosenstein, B.S., Sloan, J., Theriault, A., Vikram, B. (2016). Overview of the American Society for Radiation Oncology–National Institutes of Health–American Association of Physicists in Medicine Workshop 2015: Exploring Opportunities for Radiation Oncology in the Era of Big Data.International Journal of Radiation Oncology: Biology, Physics. 95(3):873-879 (link)
- Toga, A.W., Dinov, I.D. (2015). Sharing big biomedical data. Journal of Big Data. 2(1); 1-12. (link)
- Moore, S.M., Maffitt, D.R., Smith, K.E., Kirby, J.S., Clark, K.W., Freymann, J.B., Vendt, B.A., Tarbox, L.R., Prior, F.W. (2015). De-identification of Medical Images with Retention of Scientific Research Value. RadioGraphics. 35(3); 727-35. DOI:10.1148/rg.2015140244.
- Mayo, C.S., Deasy, J.O., Chera, B.S., Freymann, J., Kirby, J.S., Hardenberg, P.H. (2016). How Can We Effect Culture Change Toward Data-Driven Medicine?International Journal of Radiation Oncology: Biology, Physics. 95(3); 916-21. (link)
- Kirby, J., Tarbox, L., Freymann, J., Jaffe, C., Prior, F. (2015). "TU-AB-BRA-03: The Cancer Imaging Archive: Supporting Radiomic and Imaging Genomic Research with Open-Access Data Sets."Medical physics 42(6): 3587-3587. DOI:10.1118/1.4925508
- GIllies, R.J., Kinahan, P.E., Hricak, H., (2016). Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data.Radiology, 278(2); 563-77. (link)
- Fedorov, A., Clunie, D., Ulrich, E., Bauer, C., Wahle, A., Brown, B., Onken, M., Riesmeier, J., Pieper, S., Kikinis, R., Buatti, J., Beichel, R.R. (2016). DICOM for quantitative imaging biomarker development: A standards based approach to sharing of clinical data and structured PET/CT analysis results in head and neck cancer research. PeerJ, 4(e2057). (link)
- Commean, P.K., Rathmell, J.M., Clark, K.W., Maffitt, D.R., Prior, F.W. (2015). A Query Tool for Investigator Access to the Data and Images of the National Lung Screening Trial. Journal of Digital Imaging. 1-9. (paper)
- Bourne, P.E. (2015). DOIs for DICOM Raw Images: Enabling Science Reproducibility. Radiology. 275(1); 3-4. link.
- Armato, S.G., Hadjiiski, L., Tourassi, G.D., Drukker, K., Giger, M.L., Li, F., Redmond, G., Farahani, K., Kirby, J.S., Clarke, L.P. (2015). Special Section Guest Editorial: LUNGx Challenge for computerized lung nodule classification: reflections and lessons learned. Journal of Medical Imaging. 2(2); DOI:10.1117/1.JMI.2.2.020103
- Herskovits, E.H. (2014). Quantitative Radiology: Applications to Oncology. Emerging Applications of Molecular Imaging to Oncology. 124; 1-30. (10.1016/B978-0-12-411638-2.00001-X)
- Gutman, D.A., Dunn Jr., W.D., Cobb, J., Stoner, R.M., Kalpathy-Cramer, J., Erickson, B. (2014) Web based tools for visualizing imaging data and development of XNATView, a zero footprint image viewer. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics. 8. (paper)
- Erickson, B.J., Fajnwaks, P., Langer, S.G., and Perry, J. (2014) Multisite Image Data Collection and Management Using the RSNA Image Sharing Network., Translational oncology, 7(1); 36-39. (paper)
- Prior, F.W., Clark, K., Commean, P., Freymann, J., Jaffe, C., Kirby, J., Moore, S., Smith, K., Tarbox, L., Vendt, B. (2013) TCIA: an information resource to enable open science. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE.(paper)
- Clark, K., Vendt, B., Smith, K., Freymann, J., Kirby, J., Koppel, P., Moore, S., Phillips, S., Maffitt, D., Pringle, M., Tarbox, L., Prior, F. (2013). The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository, Journal of Digital Imaging, 26(6), 1045-1057. (10.1007/s10278-013-9622-7)
- Villani, L., and Prati, R.C. (2012). Classificação Multirrótulo na Anotação Automática de Nódulo Pulmonar Solitário.Congresso Brasileiro de Informática em Saúde, Citado na. (paper)
- Mongkolwat, P., Channin, D.S., Kleper, V., Rubin, D.L. (2012). Informatics in Radiology: An Open-Source and Open-Access Cancer Biomedical Informatics Grid Annotation and Image Markup Template Builder. Radiographics, 32(4); 1223-32. (10.1148/rg.324115080).
- Jaffe, C.C. (2012). Imaging and Genomics: Is There a Synergy?Radiology. 264(2); 329-31.(10.1148/radiol.12120871).
Freymann, J.B., Kirby, J.S., Perry, J.H., Clunie, D.A., Jaffe, C.C. (2012). Image data sharing for biomedical research—meeting HIPAA requirements for de-identification. Journal of Digital Imaging, 25(1). 14-24. (PMC3264712)
Radiogenomics
Li, Z.-C., Bai, H., Sun, Q., Zhao, Y., Lv, Y., Zhou, J., Liang, C., Chen, Y., Liang, D., Zheng, H. (2018). Multiregional radiomics profiling from multiparametric MRI: Identifying an imaging predictor of IDH1 mutation status in glioblastoma. Cancer Medicine. DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1863
Jansen, R. W., van Amstel, P., Martens, R. M., Kooi, I. E., Wesseling, P., de Langen, A. J., Menke-Van der Houven van Oordt, C. W., Jansen, B. H. E., Moll, A. C., Dorsman, J., Castelijns, J., de Graff, P., de Jong, M. C. (2018). Non-invasive tumor genotyping using radiogenomic biomarkers, a systematic review and oncology-wide pathway analysis. Oncotarget, 9(28), 20134-20155. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24893
- Alessandrino, F., Shinagare, A. B., Bosse, D., Choueiri, T. K., Krajewski, K. M. (2018). Radiogenomics in renal cell carcinoma. Radiology, 270(2), 464-471. DOI:10.1148/radiol.13130663 (also published in Abdominal Radiology, DOI: 10.1007/s00261-018-1624-y )
- Lee, J., Cui, Y., Sun, X., Li, B., Wu, J., Li, D., Gensheimer, M. F., Loo Jr., B. W., Diehn, M., Li, R. (2017). Prognostic value and molecular correlates of a CT image-based quantitative pleural contact index in early stage NSCLC. European Radiology, 1-11. DOI:10.1007/s00330-017-4996-4
Smits, M., & van den Bent, M. J. (2017). Imaging correlates of adult glioma genotypes. Radiology, 284(2). DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2017151930
Lehrer, M., Bhadra, A., Ravikumar, V., Chen, J. Y., Wintermark, M., Hwang, S. N., Holder, C. A., Huang, E. P., Fevrier-Sullivan, B., Freymann, J. B., Rao, A., & TCGA Glioma Phenotype Research Group. (2017). Multiple-response regression analysis links magnetic resonance imaging features to de-regulated protein expression and pathway activity in lower grade glioma. Oncoscience, 4, 57-66. doi:10.18632/oncoscience.353
- Demerath, T., Simon-Gabriel, C.P., Kellner, E., Schwarzwald, R., Lange, T., Heiland, D.H., Reinacher, P., Staszewski, O., Mast, H., Kiselev, V.G., Egger, K., Urbach, H., Weyerbrock, A., Mader, I. (2017). Mesoscopic imaging of glioblastomas: Are diffusion, perfusion and spectroscopic measures influenced by the radiogenetic phenotype? Neuroradiology Journal, 30(1); 36-47. DOI:10.1177/1971400916678225
Liu, T.T., Achrol, A.S., Mitchell, L.A., Rodriguez, S.A., Feroze, A., Iv, M., Kim, C., Chaudhary, N., Gevaert, O., Stuart, J.M., Harsh, G.R., Chang, S.D., Rubin, D.L. (2016). Magnetic resonance perfusion image features uncover an angiogenic subgroup of glioblastoma patients with poor survival and better response to antiangiogenic treatment. Neuro-Oncology, 1-11. DOI:10.1093/neuonc/now270
Schrock, M., Batar, B., Lee, J., Druck, T., Ferguson, B., Cho, J., Akakpo, K., Hagrass, H., Heerema, N., Xia, F. (2016). Wwox–Brca1 interaction: role in DNA repair pathway choice. Oncogene, 1-13. DOI:10.1038/onc.2016.389.
Song, S.E., Bae, M.S., Chang, J.M., Cho, N., Ryu, H.S., Moon, W.K. (2016). MR and mammographic imaging features of HER2-positive breast cancers according to hormone receptor status: a retrospective comparative study. Acta Radiologica. 58(7), 792-799. DOI:10.1177/0284185116673119
McCann, S.M., Jiang, Y., Fan, X., Wang, J. Antic, T., Prior, F., VanderWeele, D., Oto, A. Quantitative Multiparametric MRI Features and PTEN Expression of Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study. American Journal of Roentgenology 206(3); 559-565 DOI:10.2214/AJR.15.14967
Katrib, A., Hsu, W., Bui, A., Xing, Y. (2016). “Radiotranscriptomics”: A synergy of imaging and transcriptomics in clinical assessment.Quantitative Biology. 1-12. DOI:10.1007/s40484-016-0061-6
- Bai, H.X., Lee, A.M., Yang, L., Zhang, P., Davatzikos, C., Maris, J.M., Diskin, S.J. (2016). Imaging genomics in cancer research: Limitations and promises.The British Journal of Radiology, 89(1061); DOI:10.1259/bjr.20151030
Zhu, Y., H. Li, et al. (2015). TU-CD-BRB-06: Deciphering Genomic Underpinnings of Quantitative MRI-Based Radiomic Phenotypes of Invasive Breast Carcinoma.Medical physics 42(6): 3603-3603. DOI: 10.1118/1.4925591
Tomczak, K., Czerwińska, P., Wiznerowicz, M. (2015). The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): an immeasurable source of knowledge.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 19(1A); A68-A77. DOI:10.5114/wo.2014.47136
- Shinegare, A.B., Vikram, R., Jaffe, C., Akin, O., Kirby, J., Huang, E., Freymann, J., Sainani, N.I., Sadow, C.A., Bathala, T.K., Rubin, D.L., Oto, A., Heller, M.T., Surabhi, V.R., Katabathina, V., Silverman, S.G. (2015). Radiogenomics of clear renal cell carcinoma: Preliminary Findings of The Cancer Genome Atlas-Renal Cell Carcinoma (TCGA-RCC) Imaging Research Group.Abdominal Imaging, 40(6). 1684-1692. DOI:10.1007/s00261-015-0386-z
Pope, W.B. (2015). Genomics of Brain Tumor Imaging. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America. 25(1); 105-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.nic.2014.09.006
- Gutman, D.A., Dunn Jr., W.D., Grossmann, P., Cooper, L.A., Holder, C.A., Ligon, K.L., Alexander, B.M., Aerts, H.J. (2015). Somatic mutations associated with MRI-derived volumetric features in glioblastoma.Neuroradiology, 57(12); 1227-1237. DOI: 10.1007/s00234-015-1576-7
Feldman, M., Piazza, M.G., Edwards, N.A., Ray, Chaudhury, A., Maric, D., Merrill, M.J., Zhuang, Z., Chittiboina, P. (2015). 137 Somatostatin Receptor Expression on VHL-Associated Hemangioblastomas Offers Novel Therapeutic Target.Neurosurgery 62. (CN_suppl_1); 209-210. DOI: 10.1227/01.neu.0000467099.84064.25
- Colen R, Foster I, Gatenby R, Giger ME, Gillies R, Gutman D, Heller M, Jain R, Madabhushi A, Madhavan S, Napel S, Rao A, Saltz J, Tatum J, Verhaak R, Whitman G. (2014). NCI Workshop Report: Clinical and Computational Requirements for Correlating Imaging Phenotypes with Genomics Signatures. Translational Oncology. 7(5); 556-69. DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2014.07.007
- Rao A. (2013). Exploring relationships between multivariate radiological phenotypes and genetic features: A case-study in Glioblastoma using the Cancer Genome Atlas, Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), DOI: 10.1109/GlobalSIP.2013.6736815
Gevaert, O., Xu, J., Hoang, C.D., Leung, A.N., Xu, Y., Quon, A., Rubin, D.L., Napel, S., Plevritis, S.K. (2012) Non-small cell lung cancer: identifying prognostic imaging biomarkers by leveraging public gene expression microarray data--methods and preliminary results. Radiology. 264(2); 387-96. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12111607
Radiomics
- Lojzim, J. M., & Fries, M. (2017, August). Brain tumor Segmentation using morphological processing and the discrete wavelet transform. Journal of Young Investigators, 33(2), 55-62. DOI: 10.22186/jyi.33.3.55-62
Chaddad, A., Sabri, S., Niazi, T., & Abdulkarim, B. (2018). Prediction of survival with multi-scale radiomic analysis in glioblastoma patients. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 1-14. doi:10.1007/s11517-018-1858-4
Drukker, K., Li, H., Antropova, N., Edwards, A., Papaioannou, J., & Giger, M. L. (2018). Most-enhancing tumor volume by MRI radiomics predicts recurrence-free survival "early on" in neoadjuvant treatment of breast cancer. Cancer Imaging, 18(1). DOI:10.1186/s40644-018-0145-9
Reeves, A. P., Xie, Y., & Liu, S. (2018). Automated image quality assessment for chest CT scans. Medical Physics, 45(2), 561-578. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12729
AlBadawy, E. A., Saha, A., & Mazurowski, M. A. (2018). Deep learning for segmentation of brain tumors: Impact of cross-institutional training and testing. Medical Physics. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12752
Larue, R. T. H. M., Van De Voorde, L., van Timmeren, J. E., Leijenaar, Ralph T. H., Berbee, M., Sosef, M. N., Schreurs, W. M. J., van Elmpt, W., Lambin, P. (2017). 4DCT imaging to assess radiomics feature stability: An investigation for thoracic cancers. Radiotherapy and Oncology. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.07.023
Sutton, E. J., Huang, E. P., Drukker, K., Burnside, E. S., Li, H., Net, J. M., Rao, A., Whitman, G. J., Zuley, M., Ganott, M., Bonaccio, E., Giger, M. L., Morris, E. A. (2017). Breast MRI radiomics: Comparison of computer- and human-extracted imaging phenotypes. European Radiology Experimental. DOI: 10.1186/s41747-017-0025-2
Vani, N., Swomya, A., & Jayamma, N. (2017). MRI Brain tumor classification using support vector machine. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 1724-1729. DOI: 10.1109/SCEECS.2014.6804439
- Beichel, R.R., Smith, B.J., Bauer, C., Ulrich, E.J., Ahmadvand, P., Budzevich, M.M., Gillies, R.J., Goldgof, D., Grkovski, M., Hamarneh, G., Huang, Q., Kinahan, P.E., Laymon, C.M., Mountz, J.M., Muzi, J.P., Muzi, M., Nehmeh, S., Oborski, M.J., Tan, Y., Zhao, B., Sunderland, J.J., Buatti, J.M. (2017). Multi-site quality and variability analysis of 3D FDG PET segmentations based on phantom and clinical image data. Med. Phys. 44(2); 479-496. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12041
- Vallières, M., Kay-Rivest, E., Perrin, L.J., Liem, X., Furstoss, C., Aerts, H.J.W.L., Khaouam, N., Nguyen-Tan, P.F., Want, C.-S., Sultanem, K., Seuntjens, J., Naqa, I.E. (2017). Radiomics strategies for risk assessment of tumour failure in head-and-neck cancer. Scientific Reports, (arXiv 1703.08516)
- Paredes, D., Saha, A., Mazurowski, M.A.(2017). Deep learning for segmentation of brain tumors: can we train with images from different institutions?SPIE Medical Imaging: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, DOI: 10.1117/12.2255696
- Kumar, S., Dharun. (2017). Combination of fuzzy c-means clustering and texture pattern matrix for brain MRI segmentation. Biomedical Research, 28(5)
- Nabizadeh N, Kubat M. Automatic Tumor Segmentation in Single-Spectral MRI Using A Texture-Based and Contour-Based Algorithm. ScienceDirect, 77: 1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.01.036
Kaur, T., Saini, B.S., Gupta, S. (2016). A joint intensity and edge magnitude-based multilevel thresholding algorithm for the automatic segmentation of pathological MR brain images. Neural Computing and Applications. 1-24. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-016-2751-4
Song, J., Liu, Z., Zhong, W., Huang, Y., Ma, Z., Dong, D., Liang, C., Tian, J. (2016). Non-small cell lung cancer: quantitative phenotypic analysis of CT images as a potential marker of prognosis. Scientific Reports. 6:38282:1-9. DOI: 10.1038/srep38282
Crawford, L., Monod, A., Chen, A.X., Mukherjee, S., Rabadán, R. (2016). Topological Summaries of Tumor Images Improve Prediction of Disease Free Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme. arXiv preprint arXiv:161106818.
- Korfiatis, P., Kline, T.L., Erickson, B.J. (2016). Automated Segmentation of Hyperintense Regions in FLAIR MRI Using Deep Learning. J Tomography, 2(4) 334-340 DOI: 10.18383/j.tom.2016.00166
Zheng, C., Wang, X., Feng, D. (Eds.). (2016). Topology guided demons registration with local rigidity preservation. 2016 IEEE 38th Annual International Conference Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2016.7590913
Kotrotsou, A., Zinn, P.O., Colen, R.R. (2016). Radiomics in Brain Tumors: An Emerging Technique for Characterization of Tumor Environment. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Clinics of North America. 24(4); 719-29. DOI: 10.1016/j.mric.2016.06.006
- Zhao, B., Tan, Y., Tsai, W.Y., Qi, J., Xie, C., Lu, L., Schwartz, L.H. (2016). Reproducibility of radiomics for deciphering tumor phenotype with imaging. Scientific Reports. 6:23428. DOI: 10.1038/srep23428
- Li, H., Zhu, Y., Burnside, E.S., Huang, E., Drukker, K., Hoadley, K.A., Fan, C., Conzen, S.D., Zuley, M., Net, J.M., Sutton, E., Whitman, G.J., Morris, E., Perou, C.M., Ji, Y., Giger, M.L. (2016). Quantitative MRI radiomics in the prediction of molecular classifications of breast cancer subtypes in the TCGA/TCIA data set. npj Breast Cancer.DOI: 10.1038/npjbcancer.2016.12
- Grossmann, P., Gutman, D.A., Dunn Jr., W.D., Holder, C.A., Aerts, H.J.W.L. (2016). Imaging-genomics reveals driving pathways of MRI derived volumetric tumor phenotype features in Glioblastoma. BMC Cancer. 16(611). DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2659-5
- Zhu, Y., Li, H., Guo, W., Drukker, K., Lian, L., Giger, M.L., Ji, Y. (2015). Deciphering Genomic Underpinnings of Quantitative MRI-based Radiomic Phenotypes of Invasive Breast Carcinoma. Scientific Reports. 5(17787). DOI: 10.1038/srep17787
- Rajakumar, K., Muttan, S., Deepa, G., Revathy, S., Priya, B.S. (2015). Intelligent texture feature extraction and indexing for MRI image retrieval using curvelet and PCA with HTF. Advances in Natural and Applied Sciences. 9(6 SE) 506-513.DOI: (link)
Parmar, C., Leijenaar, R.T.H., Grossmann, P., Valazquez, E.R., Bussink, J., Rietveld, D., Rietbergen, M.M., Haibe-Kains, B., Lambin, P., Aerts, H.J.W.L. (2015). Radiomic feature clusters and Prognostic Signatures specific for Lung and Head &Neck cancer.Scientific Reports. 5(11044) DOI: 10.1038/srep11044
- Parmar, C., Grossmann, P., Bussink, J., Lambin, P., Aerts, H.J.W.L. (2015). Machine Learning methods for Quantitative Radiomic Biomarkers. Scientific Reports, 5(13087). DOI: 10.1038/srep13087
- Chaddad, A., Tanougast, C. (2015), High-Throughput Quantification of Phenotype Heterogeneity Using Statistical Features. Advances in Bioinformatics, 15(728164). DOI: 10.1155/2015/728164
- Chaddad, A. (2015). Automated Feature Extraction in Brain Tumor by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Using Gaussian Mixture Models. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2015(868031). DOI: 10.1155/2015/868031
- Dhara, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Khandelwal, N. (2013). 3d texture analysis of solitary pulmonary nodules using co-occurrence matrix from volumetric lung CT images. Medical Imaging 2013: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 8670. DOI: 10.1117/12.2007016
Dhara, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, S., Alam, N., Khandelwal, N. (2013). Measurement of spiculation index in 3D for solitary pulmonary nodules in volumetric lung CT images. Medical Imaging 2013: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 8670. DOI: 10.1117/12.2006970
Quantitative Imaging: Pathology Microscopy
Saltz J, Gupta R, Hou L, Kurc T, Singh P, Nguyen V, Samaras D, Shroyer KR, Zhao T, Batiste R, Van Arnam J, Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, Shmulevich I, Rao AUK, Lazar AJ, Sharma A, Thorsson V. Spatial Organization and Molecular Correlation of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Using Deep Learning on Pathology Images. Cell Rep.
2018;23(1):181-93 e7. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.086- Gutman, D.A., Cobb, J., Somanna, D., Park, Y., Wang, F., Kurc, T., Saltz, J.H., Brat, D.J., Cooper, L.A. (2013) Cancer Digital Slide Archive: an informatics resource to support integrated in silico analysis of TCGA pathology data. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 20(6); 1091-1098. doi:10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001469 (paper)
Algorithm Development
- Yassine, A.-A., Lilge, L., & Betz, V. (2018). Optimizing interstitial photodynamic therapy with custom cylindrical diffusers. Journal of Biophotonics. DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201800153
Men, K., Geng, H., Cheng, C., Zhong, H., Huang, M., Fan, Y., Plastaras, J. P., Lin, A., Xiao, Y. (2018). More accurate and efficient segmentation of organs-at-risk in radiotherapy with Convolutional Neural Networks Cascades. Medical Physics. DOI: 10.1002/mp.13296
Edalati-rad, A., & Mosleh, M. (2018). Improving brain tumor diagnosis using MRI segmentation based on collaboration of beta mixture model and learning automata. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 1-13. DOI:10.1007/s13369-018-3320-1
Taghanaki, S. A., Duggan, M., Ma, H., Hou, X., Celler, A., Benard, F., Hamarneh, G. (2017). Segmentation-free direct tumor volume and metabolic activity estimation from PET scans. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 63, 53-56. DOI: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2017.12.004
Y Ren, J Ma, J Xiong, Y Chen, L Lu, J Zhao (2018) Improved False Positive Reduction by Novel Morphological Features for Computer-Aided Polyp Detection in CT Colonography. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. DOI: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2808199
- Babu, J. S., Mathew, S., & Simon, R. (2017). Biomedical image retrieval using LBWP. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 4(9), 839-843. https://www.irjet.net/archives/V4/i9/IRJET-V4I9147.pdf
Hostetter, J. M., Morrison, J. J., Morris, M., Jeudy, J., Wang, K. C., & Siegel, E. (2017). Personalizing lung cancer risk prediction and imaging follow-up recommendations using the National Lung Screening Trial dataset. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 24(6), 1046-1051. DOI:10.1093/jamia/ocx012
- Mason J, Perelli A, Nailon W, Davies M. (2017) Can Planning Images Reduce Scatter in Follow-Up Cone-Beam CT? arXiv 1703.07179
Hsieh KL-C, Tsai R-J, Teng Y-C, Lo C-M. Effect of a computer-aided diagnosis system on radiologists' performance in grading gliomas with MRI. PloS one. 2017;12(2):e0171342 (link)
Hsieh KL-C, Lo C-M, Hsiao C-J. Computer-aided grading of gliomas based on local and global MRI features. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. 2017;139:31-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.10.021
Yang H, Liu F, Wang Z, Tang H, Sun S, Sun S. Research on the Content-Based Classification of Medical Image. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics. 2017;7(1):129-36. (link)
Rezaie AA, Habiboghli A. Detection of Lung Nodules on Medical Images by the Use of Fractal Segmentation. International Journal of Interactive Multimedia and Artificial Inteligence. 2017;4(Special Issue on 3D Medicine and Artificial Intelligence):15-9. (link)
Chen H, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Liao P, Li K, Zhou J, Wang G. Low-dose CT via convolutional neural network. Biomedical Optics Express. 2017;8(2):679-94.(link)
- Vallières M, Freeman C, Skamene S, El Naqa I. A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Physics in medicine and biology. 2015;60(14):5471.
- Kazdal S, Dogan B, Camurcu AY, editors. Computer-aided detection of brain tumors using image processing techniques. Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 2015 23th; 2015: IEEE.
- Gupta A, Martens O, Le Moullec Y, Saar T, editors. A tool for lung nodules analysis based on segmentation and morphological operation. Intelligent Signal Processing (WISP), 2015 IEEE 9th International Symposium on; 2015: IEEE.
- Benninghoff H, Garcke H. Segmentation of Three-dimensional Images with Parametric Active Surfaces and Topology Changes. arXiv:1506.07136. 2015.
- Zabala-Travers S, Choi M, Cheng W-C, Badano A. Effect of color visualization and display hardware on the visual assessment of pseudocolor medical images. Medical Physics. 2015;42(6):2942-54.
- Guvenis A, Koc A. OPTIMISING DELINEATION ACCURACY OF TUMOURS IN PET FOR RADIOTHERAPY PLANNING USING BLIND DECONVOLUTION. Radiation Protection Dosimetry. 2015:ncv110.
- Grove O, Berglund AE, Schabath MB, Aerts HJ, Dekker A, Wang H, Velazquez ER, Lambin P, Gu Y, Balagurunathan Y. Quantitative Computed Tomographic Descriptors Associate Tumor Shape Complexity and Intratumor Heterogeneity with Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. PloS one. 2015;10(3).
- Buerger C, Sénégas J, Kabus S, Carolus H, Schulz H, Agarwal H, Turkbey B, Choyke P, Renisch S. Comparing nonrigid registration techniques for motion corrected MR prostate diffusion imaging. Medical physics. 2015;42(1):69-80.
- Abedini M, Codella N, Connell J, Garnavi R, Merler M, Pankanti S, Smith J, Syeda-Mahmood T. A generalized framework for medical image classification and recognition. IBM Journal of Research and Development. 2015;59(2/3):1:18.
- Blessy SPS, Sulochana CH. Performance analysis of unsupervised optimal fuzzy clustering algorithm for MRI brain tumor segmentation. Technology and Health Care. 2014.
- ElNawasany AM, Ali AF, Waheed ME. A Novel Hybrid Perceptron Neural Network Algorithm for Classifying Breast MRI Tumors. Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications: Springer; 2014. p. 357-66.
- Hong S, Huang Y, Cao Y, Chen X, Han J-DJ. Approaches to uncovering cancer diagnostic and prognostic molecular signatures. Molecular & Cellular Oncology. 2014.
- Codella N, Connell J, Pankanti S, Merler M, and Smith JR. Automated Medical Image Modality Recognition by Fusion of Visual and Text Information. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. 2014, Springer. 487-495. (link)
- Ertugrul OF. Adaptive Texture Energy Measure Method. International Journal of Intelligent Information Systems. 2014. 3(2):13-18. DOI:10.11648/j.ijiis.20140302.11 (link)
- Kawa J, Juszczyk J, Pyciński B, Badura P, Pietka E. Radiological Atlas for Patient Specific Model Generation. Information Technologies in Biomedicine, 2014 4:69-82. 10.1007/978-3-319-06596-0_7. (link)
- Kowalik-Urbaniak I, Brunet D, Wang J, Koff D, Smolarski-Koff N, Vrscay ER, Wallace B, Wang Z. The quest for ‘diagnostically lossless’ medical image compression: a comparative study of objective quality metrics for compressed medical images. SPIE Medical Imaging. 2014. Vol. 9073. International Society for Optics and Photonics. DOI:10.1117/12.2043196 (link)
- Naresh P and Shettar R. Image Processing and Classification Techniques for Early Detection of Lung Cancer for Preventive Health Care: A Survey. International Journal of Recent Trends in Engineering & Technology, 2014. 11:595-601 (link)
- Patel NP, Parmar SK, and Jain KR. Swift Pre Rendering Volumetric Visualization of Magnetic Resonance Cardiac Images based on Isosurface Technique. Procedia Technology, 2014. 14:422-429. DOI:10.1016/j.protcy.2014.08.054 (link)
- Roy S, Brown MS, and Shih GL. Visual Interpretation with Three-Dimensional Annotations (VITA): Three-Dimensional Image Interpretation Tool for Radiological Reporting. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2014. 27(1):49-57. DOI: 10.1007/s10278-013-9624-5 (link)
Roth HR, Lu L, Seff A, Cherry KM, Hoffman J, Wang S, Liu J, Turkbey E, Summers RM. A new 2.5 D representation for lymph node detection using random sets of deep convolutional neural network observations. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2014: Springer; 2014. p. 520-7.
- Sivakumar S, and Chandrasekar C. A Study on Image Denoising for Lung CT Scan Images.International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational and Applied Sciences, 2014. 7(1):86-91 (link)
Seff A, Lu L, Cherry KM, Roth HR, Liu J, Wang S, Hoffman J, Turkbey EB, Summers RM. 2d view aggregation for lymph node detection using a shallow hierarchy of linear classifiers. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2014: Springer; 2014. p. 544-52.
- Harmon S, Wendelberger B, and Jeraj R. SU-E-J-98: Radiogenomics: Correspondence Between Imaging and Genetic Features Based On Clustering Analysis. Medical Physics, 2014. 41(6): p. 178-178. DOI:10.1118/1.4888150 (link)
- Krishnakumar V. and Parthiban L. Performance Analysis of Denoising in MR Images with Double Density Dual Tree Complex Wavelets, Curvelets and NonSubsampled Contourlet Transforms. Annual Review & Research in Biology, 2014. 4(19):2938-2956. DOI:10.9734/ARRB/2014/9131#sthash.qFePVdL1.dpuf (link)
- Codella N, Merler M. IBM TJ Watson Research Center. Semantic Model Vector for ImageCLEF2013. June 18, 2014. (link)
- Agostinelli F, Anderson MR, and Lee H. Adaptive Multi-Column Deep Neural Networks with Application to Robust Image Denoising. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2013. (link)
Agostinelli F, Anderson MR, Lee H, editors. Robust Image Denoising with Multi-Column Deep Neural Networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2013.
- Breseman K, Lee C, Bloch BN, and Jaffe C. Constructing 3D-Printable CAD Models of Prostates from MR Images. Bioengineering Conference (NEBEC), 39th Annual Northeast , IEEE, 27-28. 5-7 April 2013. DOI:10.1109/NEBEC.2013.8
- Buckler A, Liu TT, Savig E, Suzek BE, Rubin DL, and Paik D. Quantitative Imaging Biomarker Ontology (QIBO) for Knowledge Representation of Biomedical Imaging Biomarkers. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2013. 26(4):630-641. DOI:10.1007/s10278-013-9599-2 (link)
- Heyns M, Breseman K, Lee C, Bloch BN, Jaffe C, and Xiang H. Design of a Patient-Specific Radiotherapy Treatment Target. Bioengineering Conference (NEBEC), 2013 39th Annual Northeast. 2013.171-172. IEEE. DOI:10.1109/NEBEC.2013.75
- Kumar A, Kim J, Cai W, Fulham M, and Feng D. Content-Based Medical Image Retrieval: A Survey of Applications to Multidimensional and Multimodality Data. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2013. 26(6):1025-1039. DOI: 10.1007/s10278-013-9619-2.(link)
- Lundström C. vPSNR: a visualization-aware image fidelity metric tailored for diagnostic imaging. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2013. 8(3):437-450. DOI: 10.1007/s11548-012-0792-4 (link)
- Olmedo I, Guerra Perez Y, Johnson JF, Raut L, Hoe DHK. Image segmentation on GPGPUs: a cellular automata-based approach. Proceedings of the 2013 Summer Computer Simulation Conference. Society for Modeling & Simulation International. 2013. 51. (link)
- Pambrun JF, Noumeir R. Compressibility variations of JPEG2000 compressed computed tomography. Conference Proceedings, 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2013:3375-3378. DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610265 (link)
- Roozgard A, Barzigar N, Verma P, and Cheng S. 3D medical image denoising using 3D block matching and low-rank matrix completion. Signals, Systems and Computers, Asilomar Conference, 3-6 Nov. 2013, 253 – 257 IEEE. DOI:10.1109/ACSSC.2013.6810271
- Yankeelov TE, Atuegwu N, Hormuth D, et al. Clinically Relevant Modeling of Tumor Growth and Treatment Response. Sci Transl Med. 2013 May 29;5(187):187ps9 DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005686 (link) .
- Huang LC, Yseng LY, Hwang MS. A reversible data hiding method by histogram shifting in high quality medical images. Journal of Systems and Software 2013 March;86(3):716-27 DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2012.11.024 (link)
- Pheng HS and Shamsuddin SM. Texture classification of lung computed tomography images. 2012 International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing. 2013. Vol. 8768. International Society for Optics and Photonics. DOI:10.1117/12.2011108 (link)
- Barzigar N, Roozgard A, Verma P, Cheng S. Removing Mixture Noise from Medical Images Using Block Matching Filtering and Low-Rank Matrix Completion. Healthcare Informatics, Imaging and Systems Biology, IEEE International Conference. 2012.134. DOI:10.1109/HISB.2012.59 (link)
- Otake Y, Schafer S, Stayman JW, Zbijewski W, Kleinszig G, Graumann R, Khanna AJ, Siewerdsen JH. Automatic localization of target vertebrae in spine surgery using fast CT-to-fluoroscopy (3D-2D) image registration. SPIE Medical Imaging, 2012. Volume: 8316. International Society for Optics and Photonics. DOI:10.1117/12.911308 (link)
- Roozgard A, Cheng AS, Liu H. Malignant nodule detection on lung ct scan images with kernel rx-algorithm. Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), 2012 IEEE-EMBS International Conference on 5-7 Jan. 2012 499 – 502. IEEE. DOI: 10.1109/BHI.2012.6211627.
- Biancardi AM, Jirapatnakul AC, Reeves AP. A comparison of ground truth estimation methods. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2010. 5(3):295-305. DOI: 10.1007/s11548-009-0401-3 (link)
- Soysal OM, Chen P, Schneider H. An Image Processing Tool for Efficient Feature Extraction in Computer-Aided Detection Systems. Granular Computing (GrC) IEEE International Conference 2010. 14-16 Aug. 438-442. DOI:10.1109/GrC.2010.128
- Tseng LY and Huang LC. Automatic fissure detection in CT images based on the genetic algorithm. Machine Learning and Cybernetics (ICMLC), International Conference. IEEE. 2010. 5: 2583 – 2588. DOI: 10.1109/ICMLC.2010.5580871
Kumar, D., A. Wong, et al. (2015). Lung Nodule Classification Using Deep Features in CT Images. Computer and Robot Vision (CRV), 2015 12th Conference on, IEEE.
Kanas, V. G., E. I. Zacharaki, et al. (2015). "A low cost approach for brain tumor segmentation based on intensity modeling and 3D Random Walker." Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 22: 19-30.
Magdy, E., N. Zayed, et al. (2015). "Automatic Classification of Normal and Cancer Lung CT Images Using Multiscale AM-FM Features." International Journal of Biomedical Imaging 2015.
Zayed, N. and H. A. Elnemr (2015). "Statistical Analysis of Haralick Texture Features to Discriminate Lung Abnormalities." International Journal of Biomedical Imaging 2015.
- Chaddad, A. and C. Tanougast "High-Throughput Quantification of Phenotype Heterogeneity Using Statistical Features." Advances in Bioinformatics 2015. DOI: 10.1155/2015/728164
- Li M, Miller K, Joldes GR, Kikinis R, Wittek A. Biomechanical model for computing deformations for whole-body image registration: A meshless approach. International. Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering. 2016. DOI: 10.1002/cnm.2771
Radiation Oncology
Jaffray D, Chung C, Coolens C, Foltz W, Keller H, Menard C, Milosevic M, Publicover J, Yeung I, editors. Quantitative imaging in radiation oncology: An emerging science and clinical service. Seminars in Radiation Oncology; 2015: Elsevier.
Theses
Jonathan Hugh Mason.(2018) Quantitative Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Reconstruction for Radiotherapy Planning . University of Edinburgh. (link to thesis)
Golan, R. (2018). DeepCADe: A deep learning architecture for the detection of lung nodules in CT scans. (link to thesis)
Großmann, P. B. H. J. (2018) Defining the biological and clinical basis of radiomics: towards clinical imaging biomarkers. Datawyse / Universitaire Pers Maastricht. DOI: 10.26481/dis.20180308pg (link to thesis)
- Webb, G. (2018). A Gaussian mixture model based level set method for volume segmentation in medical images. Linköping, Sweden. (link to thesis)
Androutsou, T. Clinical Decision Support System for Lung Cancer Diagnosis by analysis of thoracic CT images. Carrier NTUA, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 2017. (link to thesis)
- Emirzade, Erkan. A COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM FOR LUNG CANCER DETECTION USING SVM. The Graduate School Of Applied Sciences Of Near East University, 2016. (link to thesis)
- Yu, Zexi. Co-Segmentation Methods for Improving Tumor Target Delineation in PET-CT Images. University of Saskatchewan 2016. (link to thesis)
Albalooshi FA. Self-organizing Approach to Learn a Level-set Function for Object Segmentation in Complex Background Environments. University of Dayton; 2015. (link to thesis)
Camlica Z. Image Area Reduction for Efficient Medical Image Retrieval. Waterloo, Ontario, Canada,: University of Waterloo; 2015. (link to thesis)
- Hunter L. Radiomics of NSCLC: Quantitative CT Image Feature Characterization and Tumor Shrinkage Prediction. Thesis, University of Texas; 2013. (link to thesis)
Karnayana PM. Radiogenomic correlation for prognosis in patients with glioblastoma multiformae. San Diego State University; 2013. (link to thesis)
Nabizadeh, N. Automated Brain Lesion Detection and Segmentation Using Magnetic Resonance Images. Electrical and Computer Engineering. Miami, FL, University of Miami. PhD., 2015. (link to thesis)
Wieser, H.-P. Supervised Machine Learning Approach Utilizing Artificial Neural Networks for Automated Prostate Zone Segmentation in Abdominal MR images. Klagenfurt, Austria, Fachhochschule Kärnten/Carinthia University of Applied Sciences; 2013.(link to thesis)
TCIA DOI for Analysis Datasets
- Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, et al. (2014). Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Armato SG and Drukker K, et al. (2015). SPIE-AAPM-NCI Lung Nodule Classification Challenge Dataset. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Bloch N, Rusu M, et al. (2015) NCI-ISBI 2013 Challenge: Automated Segmentation of Prostate Structures. TCIA. St. Louis, MO. (link)
- Colen RR, Wang J, et al. (2014). Glioblastoma: Imaging Genomic Mapping Reveals Sex-specific Oncogenic Associations of Cell Death. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
Fedorov A, Schwier M, Clunie D, Herz C, Pieper S, Kikinis R, Tempany C, Fennessy F. (2018) An annotated test-retest collection of prostate multiparametric MRI Scientific Data 5:180281.( link )
Gevaert O, Mitchell LA, et al. (2014). Glioblastoma multiforme: exploratory radiogenomic analysis by using quantitative image features. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Gevaert O, Xu J, et al. (2014). Non-small cell lung cancer: identifying prognostic imaging biomarkers by leveraging public gene expression microarray data--methods and preliminary results. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Grove O, Berglund AE, et al. (2015). Data from: Quantitative computed tomographic descriptors associate tumor shape complexity and intratumor heterogeneity with prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. TCIA. Saint Louis. MO. (link)
Gutman DA, Cooper LA, et al. (2014). MR Imaging Predictors of Molecular Profile and Survival: Multi-institutional Study of the TCGA Glioblastoma Data Set. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
Huang W, Li X, et al. (2014). Variations of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of breast cancer therapy response: a multicenter data analysis challenge. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO.
Jain R, Poisson LM, et al. (2014). Outcome Prediction in Patients with Glioblastoma by Using Imaging, Clinical, and Genomic Biomarkers: Focus on the Nonenhancing Component of the Tumor. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
Kalpathy-Cramer J, Napel S, et al. (2015). QIN multi-site collection of Lung CT data with Nodule Segmentations. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Lee J, Narang S, et al. (2015). Spatial Habitat Features derived from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging data from Glioblastoma Multiforme cases. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Liu F, Hernandez-Cabronero M, et al. (2016). Image Data Used in the Simulations of "The Role of Image Compression Standards in Medical Imaging: Current Status and Future Trends". TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Mazurowski MA, Zhang J, et al. (2014). Radiogenomic Analysis of Breast Cancer: Luminal B Molecular Subtype Is Associated with Enhancement Dynamics at MR Imaging. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
Messay T, Hardie RC, et al. (2014). Segmentation of Pulmonary Nodules in Computed Tomography Using a Regression Neural Network Approach and its Application to the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative Dataset. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
- Morris E, Burnside M, et al. (2014). TCGA Breast Phenotype Research Group Data sets. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO (link)
Roth H, Lu L, et al. (2015). A new 2.5D representation for lymph node detection in CT. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
Shinagare AB, Vikram R, et al. (2015). Radiogenomics of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Preliminary Findings of The Cancer Genome Atlas-Renal Cell Carcinoma (TCGA-RCC) Research Group. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
Vallières M, Freeman CR, et al. (2015). Data from: A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. TCIA. Saint Louis, MO. (link)
QIN
- Semmineh NB, Stokes AM, Bell LC, Boxerman JL, Quarles CC. A Population-Based Digital Reference Object (DRO) for Optimizing Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC)-MRI Methods for Clinical Trials. TOMOGRAPHY, 2017; 3(1)41-9. doi: 10.18383/j.tom.2016.00286
Farahani K, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Chenevert TL, et al. Computational Challenges and Collaborative Projects in the NCI Quantitative Imaging Network. Tomography, 2016;2(4):242-9. DOI: 10.18383/j.tom.2016.00265)
Kalpathy-Cramer J, Mamomov A, Zhao B,et al.. Radiomics of Lung Nodules: A Multi-Institutional Study of Robustness and Agreement of Quantitative Imaging Features. Tomography,2016;2(4):430-7. doi: 10.18383/j.tom.2016.00235.
Huang, W., X. Li, et al. (2014). "Variations of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of breast cancer therapy response: a multicenter data analysis challenge." Transl Oncol 7(1): 153-166. (link)
Kalpathy-Cramer J, Freymann JB, Kirby JS, et al. Quantitative Imaging Network: Data Sharing and Competitive Algorithm Validation Leveraging The Cancer Imaging Archive Translational Oncology. 2014 Feb;7(1):147-52. DOI: 10.1593/tlo.13862. (link)
- Clarke LP, Nordstrom RJ, Zhang H, Tandon P, et al. The Quantitative Imaging Network: NCI’s Historical Perspective and Planned Goals Translational Oncology. 2014 Feb;7(1):1-4. DOI: 10.1593/tlo.13832. (link)
- Levy MA, Freymann JB, Kirby JS, et al. Informatics methods to enable sharing of quantitative imaging research data. Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2012 Nov;30(9):1249-56. DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.04.007. Epub 2012 Jul 6. (link)
Publications relating to specific data collections:
Collection: CT Colonography
Lin AY, Du P, Dinning PG, Arkwright JW, Kamp JP, Cheng LK, Bissett IP, O'Grady G. High resolution anatomic correlation of cyclic motor patterns in the human colon: Evidence of a rectosigmoid brake. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2017;312(5):G508-G15. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00021.2017.
Gayathri DK, Radhakrishnan R, Rajamani K. Segmentation of colon and removal of opacified fluid for virtual colonoscopy. Pattern Analysis and Applications. 2017:1-15. DOI: 10.1007/s10044-017-0614-y
- Pang S, Yu Z, Orgun MA. A Novel End-to-End Classifier Using Domain Transferred Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Biomedical Images. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. 2017. (link)
- Yahya-Zoubir B, Hamami L. et al. Automatic 3D Mesh-Based Centerline Extraction from a Tubular Geometry Form. Information Technology and Control, 2016. 45(2):156-163. (link)
- Alazmani A, Hood A, et al. Quantitative Assessment of Colorectal Morphology: Implications for Robotic Colonoscopy. Medical Engineering and Physics, 2016. 38(2):148-154. (link)
- Gayathri Devi K, Radhakrishnan R. Automatic Segmentation of Colon in 3D CT Images and Removal of Opacified Fluid Using Cascade Feed Forward Neural Network. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine. 2015;2015.
- Namías R, et al., Automatic rectum limit detection by anatomical markers correlation. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2014. 38(4):245-250.(link)
- Boone DJ, Halligan S, Roth HR, et al., CT Colonography: External Clinical Validation of an Algorithm for Computer-assisted Prone and Supine Registration. Radiology, 2013. 268(3):752-760.(link)
- Roth HR, et al., External clinical validation of prone and supine CT colonography registration in Abdominal Imaging. Computational and Clinical Applications 2012, Springer. 7601:10-19.(link)
Collection: Head-Neck Cetuximab
Gruselius, H. (2018). Generative models and feature extraction on patient images and structure data in radiation therapy. Retrieved from http://kth.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1215620&dswid=2429
Scarpelli, M., Eickhoff, J., Cuna, E., Perlman, S., & Jeraj, R. (2018). Optimal transformations leading to normal distributions of positron emission tomography standardized uptake values. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 63(3), 035021. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/aaa175
Ryalat MH, Laycock S, Fisher M, editors. Automatic Removal of Mechanical Fixations from CT Imagery with Particle Swarm Optimisation. International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering; 2017: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-56148-6_37
Collection: LIDC-IDRI
- Mackie, T. R., Jackson, E. F., & Giger, M. (2018). Opportunities and challenges to utilization of quantitative imaging: Report of the AAPM practical big data workshop. Medical Physics. DOI: 10.1002/mp.13135
- Sumathipala, Y., Shafiq, M., Bongen, E., Brinton, C., & Paik, D. (2018). Machine learning to predict lung nodule biopsy method using CT image features: A pilot study. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2018.10.006
- Cha J, Farhangi MM, Dunlap N, Amini AA. Segmentation and tracking of lung nodules via
graph‐cuts incorporating shape prior and motion from 4D CT. Medical physics. 2018;45(1):297-306. doi: 10.1002/mp.12690.
Agnes, S. A., Anitha, J., & Peter, J. D. (2018). Automatic lung segmentation in low-dose chest CT scans using convolutional deep and wide network (CDWN). Neural Computing and Applications. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-018-3877-3
Kohl, S. A., Romera-Paredes, B., Meyer, C., De Fauw, J., Ledsam, J. R., Maier-Hein, K. H., Eslami, S., Rezende, D. J., Ronneberger, O. (2018). A probabilistic U-Net for segmentation of ambiguous images. Retrieved from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1806.05034.pdf
- Kang, G., Liu, K., Hou, B., & Zhang, N. (2017). 3D multi-view convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. (Y. Deng, Ed.) PLOS One, 12(11). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188290
- Liu, F., Feng, J., Su, W., Lv, Z., Xiao, F., & Qiu, S. (2017). Normalized euclidean super-pixels for medical image segmentation. International Conference on Intelligent Computing (pp. 586-597). Springer. 10.1007/978-3-319-63315-2_51
Farag, A. A., Ali, A., Elshazly, S., & Farag, A. A. (2017). Feature fusion for lung nodule classification. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 1-10. DOI:10.1007/s11548-017-1626-1
- MC Hancock, JF Magnan. Predictive capabilities of statistical learning methods for lung nodule malignancy classification using diagnostic image features: an investigation using the Lung Image Database Consortium dataset. Proc. SPIE Medical Imaging: Computer-Aided Diagnosis (2017). International Society for Optics and Photonics. DOI: 10.1117/12.2254446
- Wang, D; Fong, S; Wong, RK.; Mohammed, S; Fiaidhi, J; Wong, KKL. Robust High-dimensional Bioinformatics Data Streams Mining by ODR-ioVFDT. Scientific Reports 7, article number 43167 DOI: 10.1038/srep43167
Mhetre RR, Sache RG. Detection of Lung Cancer Nodule on CT scan Images by using Region Growing Method. International Journal of Current Trends in Engineering & Research. 2016;2(7):215-9. (link)
Setio AAA, Traverso A, de Bel T, Berens MS, Bogaard Cvd, Cerello P, Chen H, Dou Q, Fantacci ME, Geurts B. Validation, comparison, and combination of algorithms for automaticdetection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography images: the LUNA16 challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:161208012. 2016:1-16.
- Firmino M, Angelo G, et al. Computer-aided Detection (CADe) and Diagnosis (CADx) System for Lung Cancer with Likelihood of Malignancy Biomed Eng Online (2016) 15(1):2 (link)
- Deep G, Kaur L, et al. Directional Local Ternary Quantized Extrema Pattern: A new descriptor for Biomedical Image Indexing and Retrieval Eng Sci and Tech, an International Journal (2016) (link)
- Wang W, Luo J, Yang X, Lin H. Data Analysis of the Lung Imaging Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative. Academic Radiology. 2015.
Sivakumar, S. and C. Chandrasekar (2015). "A Novel Noise Removal Method for Lung CT SCAN Images Using Statistical Filtering Techniques." International Journal of Algorithms Design and Analysis 1(1).
- Shen S, Bui AA, Cong J, Hsu W. An automated lung segmentation approach using bidirectional chain codes to improve nodule detection accuracy. Computers in biology and medicine. 2015;57:139-49.
- Messay T, Hardie RC, Tuinstra TR. Segmentation of Pulmonary Nodules in Computed Tomography Using a Regression Neural Network Approach and its Application to the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative Dataset. Medical Image Analysis. 2015.(paper)
Magdy, E., N. Zayed, et al. Automatic Classification of Normal and Cancer Lung CT Images using Multi-scale AM-FM Features. Intl Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2015. (link)
Lassen BC, Jacobs C, et al. Robust Semi-automatic Segmentation of Pulmonary Subsolid Nodules in Chest Computed Tomography Scans. Phys Med Biol (2015) 60(3):1307-1323. (link)
Kumar, D., M. J. Shafiee, et al. Discovery Radiomics for Computed Tomography Cancer Detection. arXiv e-print, 2015. (arXiv link)
Demir, Ö. and A. Yılmaz Çamurcu (2015). "Computer-aided detection of lung nodules using outer surface features." Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering 26(s1): 1213-1222.
Kumar, A., F. Nette, et al. (2014). "A Visual Analytics Approach using the Exploration of Multi-Dimensional Feature Spaces for Content-based Medical Image Retrieval IEEE J Biomed Health Inform (2014) 19(5):1734:1746 (pubmed link)
- Sivakumar S and Chandrasekar C, Lung nodule detection using fuzzy clustering and support vector machines. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2013. 5(1):179-185.(link)
- Gavrielides MA, Zeng R, Myers KJ, Sahiner B, Petrick N. Benefit of overlapping reconstruction for improving the quantitative assessment of CT lung nodule volume. Academic Radiology, 2013. 20(2):173-180. DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2012.08.014. (link)
- Aggarwal P, Vig R, and Sardana H Patient-Wise Versus Nodule-Wise Classification of Annotated Pulmonary Nodules using Pathologically Confirmed Cases. Journal of Computers, 2013. 8(9):2245-2255. (link)
- Sivakumar S and Chandrasekar C, Lungs image segmentation through weighted FCM.Recent Advances in Computing and Software Systems (RACSS), 2012 International Conference. 25-27 April 2012 pages 109-113. IEEE. DOI:10.1109/RACSS.2012.6212707 (link)
- Armato S, et al., Collaborative projects. Int J CARS, 2012. 7(1):S111-S115.
- Diciotti S, Lombardo S, Falchini M, Picozzi G, Mascalchi M. Automated segmentation refinement of small lung nodules in CT scans by local shape analysis. Biomedical Engineering, IEEE Transactions. 2011. 58(12):3418-3428. DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2167621. (link)
Raicu DS, Varutbangkul E, Furst JD, Armato SG III: Modeling semantics from image data: Opportunities from LIDC. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology 3: 83–113, 2010.
Zinovev D, Duo Y, Raicu DS, Furst JD, Armato SG III: Consensus versus disagreement in imaging research: A case study using the LIDC Database. Journal of Digital Imaging 25: 423–436, 2012.
Collection: Mouse-Mammary
These refer to the Mouse-Mammary Collection data, created before submission to TCIA
- Jansen SA et al, NMR Biomed. 2011 Aug;24(7):880-7.
- Jansen SA et al, Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R65.
- Jansen SA et al, Radiology. 2009 Nov;253(2):399-406.
- Jansen SA et al, Phys Med Biol. 2008 Oct 7;53(19):5481-93.
- Jansen SA., Ductal carcinoma in situ: magnetic resonance and ultrasound imaging in mouse models of breast cancer (Mouse.Mammary.MRI.Ultrasound.Summary.pdf).
- Jansen S., Investigating genetic events in the progression of ductal carcinoma in situ (Mouse.Mammary.Genetics.DCIS.pdf).
Collection: NLST
Please see List of NLST Publications at NIH to browse publications from this Data Collection.
Collection: NSCLC-Radiomics
- L Yang, J Yang, X Zhou, L Huang, W Zhao, T Wang, J Zhuang, J Tian. (2018) Development of a radiomics nomogram based on the 2D and 3D CT features to predict the survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. European Radiology, 2018 DOI: 10.1007/s00330-018-5770-y
- Lee, J., Cui, Y., Sun, X., Li, B., Wu, J., Li, D., Gensheimer, M. F., Loo Jr., B. W., Diehn, M., Li, R. (2017). Prognostic value and molecular correlates of a CT image-based quantitative pleural contact index in early stage NSCLC. European Radiology, 1-11. DOI: 10.1007s00330-017-4996-4
Soufi M, Arimura H, Nakamoto T, Hirose T-A, Ohga S, Umezu Y, Honda H, Sasaki T. (2018). Exploration of temporal stability and prognostic power of radiomic features based on electronic portal imaging device images. Physica Medica, 46:32-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.11.037
Patil R, Mahadevaiah G, Dekker A. An Approach Toward Automatic Classification of Tumor Histopathology of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Based on Radiomic Features. Tomography: a journal for imaging research. 2016;2(4):374-7. (link)
Collection: Phantom FDA
- Peskin AP, Dima AA, Saiprasad G. An Automated Method for Locating Phantom modules in Anthropomorphic Thoracic Phantom CT Studies. The 2012 International Conference on Image Processing, Computer Vision, and Pattern Recognition. 2012.(link)
- Gavrielides MA, Kinnard LM, Myers KJ ,Peregoy J, Pritchard WF, Zeng R, Esparza J, Karanian J, Petrick N, A resource for the assessment of lung nodule size estimation methods: database of thoracic CT scans of an anthropomorphic phantom, Optics Express , vol. 18, n.14, pp. 15244-15255, 2010. (link)
Collection: QIN Breast
- Mohammed Ammar, Saïd Mahmoudi, Drisis Stylianos. Breast Cancer Response Prediction in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Treatment Based on Texture Analysis. Procedia Computer Science, Volume 100, 2016, Pages 812-817, ISSN 1877-0509, DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.09.229
- Li X, Abramson RG, Arlinghaus LR, Kang H, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson VG, Farley J, Mayer IA, Kelley MC, Meszoely IM, Means-Powell J, Grau AM, Sanders M, Yankeelov TE. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for predicting pathological response after the first cycle of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Investigative Radiology, 2015 Apr;50(4):195-204. PMCID: PMC4471951 DOI: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000100.
Weis JA, Miga MI, Arlinghaus LR, Li X, Abramson V, Chakravarthy AB, Pendyala P, Yankeelov TE. Predicting the Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Therapy Using a Mechanically Coupled Reaction-Diffusion Model. Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;75(22):4697-707. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2945.
- Atuegwu NC, Arlinghaus L, Li X, Welch EB, Chakravarthy AB, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Integration of diffusion weighted MRI data and a simple mathematical model to predict breast tumor cellularity during neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2011; 66:1689-96. PMCID: PMC3218213
- Li, X, Welch EB, Chakravarthy B, Mayer I, Meszeoly I, Kelley M, Means-Powell J, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Statistical comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI pharmacokinetic models in human breast cancer. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2012; 68:261-71. PMCID: PMC3291742
- Smith DS, Gambrell JV, Li X, Arlinghaus LA, Quarles CC, Yankeelov TE, Welch EB. Robustness of Quantitative Compressive Sensing MRI: The Effect of Random Acquisitions on Derived Parameters for DCE and DSC-MRI. IEEE Transactions in Medical Imaging, 2012; 31:504-11. PMCID: PMC3289060
- Smith DS, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE, Welch EB. Real-time Compressive Sensing MRI Reconstruction using GPU Computing and Split Bregman Methods. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2012; 2012:864827. PMCID: PMC3296267
- Dula AN, Arlinghaus LR, Dortch RD, Dewey BE, Whisenant JE, Ayers GD, Yankeelov TE, Smith SE. Amide Proton Transfer Imaging of the Breast at 3 T: Establishing reproducibility and possible feasibility for assessing chemotherapy response. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2013; 70: 216-24. PMCID: PMC3505231
- Yankeelov TE, Peterson TE, Abramson RG, Garcia-Izquierdo D, Arlinghaus LR, Li X, Atuegwu NC, Catana C, Manning HC, Fayad ZA, Gore JC. Simultaneous PET-MRI in Oncology: A Solution Looking for a Problem? Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2012; 30:1342-56. Selected as a Top 25 paper in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2012. PMCID: PMC3466373
- Abramson RG, Arlinghaus LR, Weis JA, Li X, Dula AN, Chekmenev EY, Smith SA, Miga MI, Abramson VG, Yankeelov TE. Current and emerging quantitative magnetic resonance imaging methods for assessing and predicting the response of breast cancer to neoadjuvant therapy. Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapies, 2012; 4: 139-154. PMCID: PMC3496377
- Li X, Abramson RG, Arlinghaus LR, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson V, Mayer I, Farley J, Delbeke D, Yankeelov TE. An Algorithm for Longitudinal Registration of PET/CT Images Acquired During Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer: Preliminary Results. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Research, 2012; 16:62. PMCID: PMC3520720
- Fluckiger U, Loveless ME, Barnes SL, Lepage M, Yankeelov TE. A diffusion-compensated model for the analysis of DCE-MRI data: theory, simulations, and experimental results. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2013; 58:1983-98. PMCID: PMC3646091
- Yankeelov TE. Integrating Imaging Data into Predictive Biomathematical and Biophysical Models of Cancer. ISRN Biomathematics, 2012; Article ID 287394. PMCID: PMC3729405
- Atuegwu NC, Arlinghaus LR, Li X, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson VG, Sanders ME, Yankeelov TE. Parameterizing the Logistic Model of Tumor Growth by DW-MRI and DCE-MRI Data to Predict Treatment Response and Changes in Breast Cancer Cellularity During Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Translational Oncology, 2013; 6:253-64. PMCID: PMC3660793
- Klomp DWJ, Dula AN, Arlinghaus LR, Italiaander M, Dortch RD, Zu Z, Williams JM, Gochberg DF, Luijten PR, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE, Smith SA. Amide Proton Transfer Imaging of the Human Breast at 7 Tesla: Development and Reproducibility. NMR in Biomedicine, 2013; 26:1271-7. PMCID: PMC3726578
- Mani S, Chen Y, Li X, Arlinghaus L, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson V, Bhave SR, Levy MA, Xu H, Yankeelov TE. Machine Learning for Predicting the Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 2013; 20:688-95. PMCID: PMC3721158
- Li X, Arlinghaus LR, Ayers GD, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson RG, Abramson VG, Atuegwu N, Farley J, Mayer IA, Kelley MC, Meszoely IM, Means-Powell J, Grau AM, Sanders M, Bhave SR, Yankeelov TE. DCE-MRI Analysis Methods for Predicting the Response of Breast Cancer to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Pilot Study Findings. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2014; 71(4):1592-602. PMCID: PMC3742614
- Yankeelov TE, Atuegwu N, Hormuth D, Weis JA, Barnes SL, Miga MI, Rericha EC, Quaranta V. Clinically relevant modeling of tumor growth and treatment response. Science Translational Medicine 2013; 5:187ps9. PMCID: PMC3938952
- Abramson RG, Hoyt TL, Wilson KJ, Li X, Arlinghaus LR, Su P-F, Abramson VG, Chakravarthy AB, Yankeelov TE. Early Assessment of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy by Semi- Quantitative Analysis of High Temporal Resolution DCE-MRI: Preliminary Results. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2013 ; 31:1457-64. PMCID: PMC3807825
- Weis JA, Miga MI, Arlinghaus LA, Li X, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson VG, Farley J, Yankeelov TE. A mechanically coupled reaction-diffusion model for predicting the response of breast tumors to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Physics of Medicine and Biology, 2013; 58:5851-66. PMCID: PMC3791925
- Smith DA, Yankeelov TE, Welch EB. Potential of Compressed Sensing in Quantitative MR Imaging of Cancer. Cancer Imaging, 2013; 13:633-44. PMCID: PMC3893904
- Fluckiger JU, Li X, Whisenant JG, Peterson TE, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Using dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging data to constrain a positron emission tomography kinetic model: theory and simulations. International Journal of Biomedical Imaging, 2013; 2013:576470. PMCID: PMC3814089
- Fedorov A, Fluckiger J, Ayers GD, Li X, Gupta SN, Mulkern R, Yankeelov TE, Fennessy FM. A Comparison of Two Methods for Estimating DCE-MRI Parameters via Individual and Cohort Based AIFs in Prostate Cancer: A Step Towards Practical Implementation. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2014; 32:321-9. PMCID: PMC3965600
- Li X, Kang H, Arlinghaus LR, Abramson RG, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson VG, Farley J, Sanders M, Yankeelov TE. Analyzing Spatial Heterogeneity in DCE- and DW-MRI Parametric Maps to Optimize Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Translational Oncology, 2014; 7:14-22. PMCID: PMC3998687
- Chenevert TL, Malyarenko DI, Newitt D, Hylton N, Huang W, Li X, Tudorica A, Fedorov A, Fennessy F, Kikinis R, Arlinghaus L, Li X, Yankeelov TE, Muzi M, Marro KI, Kinahan PE, Jajamovich GH, Dyvorne HA, Taouli B, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Oborski MJ, Laymon CM, Mountz JM, Ross BD. Error in Quantitative Image Analysis Due to Platform-Dependent Image Scaling. Translational Oncology, 2014; 7:65-71. PMCID: PMC3998685
- Huang W, Li X, Chen Y, Li X, Chang M-C, Oborski MJ, Malyarenko DI, Muzi M, Jajamovich GH, Federov A, Tudorica A, Gupta S, Laymon CM, Marro KI, Dyvorne HA, Miller JV, Chenevert TL, Yankeelov TE, Mountz JM, Kinahan PE, Kikinis R, Taouli B, Fennessy F, Kalpathy-Cramer J. Variations of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Evaluation of Breast Cancer Therapy Response: A Multicenter Data Analysis Challenge. Translational Oncology, 2014; 7:153-66. PMCID: PMC3998693
- Atuegwu NC, Li X, Arlinghaus LR, Abramson RG, Williams JM, Chakravarthy AB, Abramson V, Yankeelov TE. Longitudinal, Inter-modality Registration of Quantitative Breast PET and MRI Data Acquired Before and During Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Preliminary Results. Medical Physics, 2014; 41:052302. PMCID: PMC4000383
These refer to the QIN-Breast Collection data, created before submission to TCIA
- Li X, Dawant BM, Welch EB, Chakravarthy AB, Freehardt D, Mayer I, Kelley M, Meszoely I, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Validation of an algorithm for the nonrigid registration of longitudinal breast MR images using realistic phantoms. Medical Physics, 2010; 37:2541-52. PMCID: PMC2881925
- Atuegwa NC, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Using Quantitative Imaging Data to Drive Mathematical Models of Tumor Growth and Treatment Response. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2010; 55:2429-49. PMCID: PMC2897238
- Yankeelov TE, Arlinghaus L, Li X, Gore JC. The role of magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers in clinical trials of treatment response in cancer. Seminars in Oncology, 2011; 38:16-25. PMCID: PMC3073543
- Arlinghaus L, Li X, Levy M, Smith D, Welch WB, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Current and Future Trends in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Assessments of the Response of Breast Tumors to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Journal of Oncology, 2010. pii: 919620. Epub 2010 Sep 29. PMCID: PMC2952974
- Arlinghaus LR, Welch EB, Chakravarthy AB, Farley JS, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Motion and distortion correction in diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast at 3T. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2011; 33:1063-70. PMCID: PMC3081111
- Gore JC, Manning HC, Quarles CC, Waddell KW, Yankeelov TE. Magnetic Resonance in the Era of Molecular Imaging of Cancer. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2011; 29:587-600. PMCID: PMC3285504
- Arlinghaus LR, Li X, Rahman AR, Welch EB, Xu L, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. On the Relationship Between the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Extravascular Extracellular Volume Fraction in Human Breast Cancer. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2011; 29:630-8. PMCID: PMC3100356
- Smith DS, Welch EB, Li X, Arlinghaus LD, Loveless ME, Koyama T, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. Quantitative effects of accelerated dynamic contrast enhanced MRI data using compressed sensing. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2011; 56:4933-46. PMCID: PMC3192434
- Li, X, Welch EB, Chakravarthy B, Mayer I, Meszeoly I, Kelley M, Means-Powell J, Gore JC, Yankeelov TE. A novel AIF tracking method and comparison of DCE-MRI parameters using individual and population-based AIFs in human breast cancer. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2011; 56:5753-69. PMCID: PMC3176673
Collection: QIN Breast DCE-MRI
Nowaková J, Prílepok M, Snášel V. Medical Image Retrieval Using Vector Quantization and Fuzzy S-tree. Journal of Medical Systems. 2017;41(2):18. (link)
Collection: QIN GBM DCE-MRI
- Beers, A., Chang, K., Brown, J., Zhu, X., Sengupta, D., Willke, T. L., Gerstner, E., Rosen, B., Kalpathy-Cramer, J. (2018). Anatomical DCE-MRI phantoms generated from glioma patient data. SPIE Medical Imaging. 105732(V). Houston: SPIE. DOI:10.1117/12.2294961
- Gerstner ER, Zhang Z, Fink JR, Muzi M, Hanna L, Greco E, Mintz A, Kostakoglu L, Eikman EA, Prah MA, Ellingson BM, Ratai EM, Schmainda KM, Sorensen G, Barboriak DP, Mankoff DA. ACRIN 6684: Assessment of tumor hypoxia in newly diagnosed GBM using 18F-FMISO PET and MRI. Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 15;22(20):5079-5086. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2529
- Gerstner ER, Zhang Z, Fink JR, Muzi M, Hanna L, Greco E, Mintz A, Kostakoglu L, Eikman EA, Prah M, Schmainda KM, Sorensen GA, Barboriak D, Mankoff DA. ACRIN 6684: Assessment of tumor hypoxia in newly diagnosed GBM using 18F-FMISO PET and MRI. J Clin Oncol 33(Suppl):2024. 2015.
- Fink JR, Zhang Z, Gerstner ER, Muzi M, Kostakoglu L, Mintz A, Eikman EA, Barboriak D, Mankoff DA. ACRIN 6684: Multicenter phase II assessment of tumor hypoxia in glioblastoma using 18F-Fluoromisonidazole (FMISO) PET and MRI. J Nucl Med 56(Suppl3):325. 2015.
- Fink JR, Muzi M, Peck M, Krohn KA. Multimodality Brain Tumor Imaging: MR Imaging, PET, and PET/MR Imaging. J Nucl Med 56(10):1554-1561. 2015.
- Muzi M, Fink JR, Richards TL, Marro KI, Wong T, Muzi JP, Eary JF, Rockhill JK, Krohn KA. Evaluation of PET and MR measurements to examine progression in glioma patients. J Nucl Med 55(Suppl1):1512-. 2014.
Collection: QIN HeadNeck
- Stoll M, Stoiber EM, Grimm S, Debus J, Bendl R, Giske K. Comparison of Safety Margin Generation Concepts in Image Guided Radiotherapy to Account for Daily Head and Neck Pose Variations. PloS one. 2016;11(12):e0168916. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168916
- Ahmadvand P, Duggan N, Bénard F, Hamarneh G. Tumor Lesion Segmentation from 3D PET Using a Machine Learning Driven Active Surface. MLMI 2016 in conjunction with the 19th Int'l Conference on MICCAI. (link)
- Fedorov A, Clunie D, Ulrich E, et al. (2016) DICOM for quantitative imaging biomarker development: a standards based approach to sharing clinical data and structured PET/CT analysis results in head and neck cancer research. PeerJ 4:e2057 DOI: 10.7717/peerj.2057
- Beichel RR, Van Tol M, Ulrich EJ, et al. (2016) Semiautomated segmentation of head and neck cancers in 18F-FDG PET scans: A just-enough-interaction approach. Medical Physics 43:2948–2964. DOI: 10.1118/1.4948679.
Collection: QIN Prostate
- Lavasani, S. N., Mostaar, A., & Ashtiyani, M. (2017). Automatic prostate cancer segmentation using kinetic analysis in dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. Journal of Biomedical Phsyics and Engineering. DOI: 10.22086/jbpe.v0i0.555
- Fedorov A, Fluckiger J, Ayers GD, Li X, Gupta SN, Tempany C, Mulkern R, Yankeelov TE, Fennessy FM. A comparison of two methods for estimating DCE-MRI parameters via individual and cohort based AIFs in prostate cancer: A step towards practical implementation. Magnetic resonance imaging. 2014;32(4):321-9.
- Hegde JV, Mulkern RV, Panych LP, Fennessy FM, Fedorov A, Maier SE, Tempany C. Multiparametric MRI of prostate cancer: An update on state‐of‐the‐art techniques and their performance in detecting and localizing prostate cancer. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 2013;37(5):1035-54.
- Benalcázar, M. E., M. Brun, et al. (2015). Automatic Design of Window Operators for the Segmentation of the Prostate Gland in Magnetic Resonance Images. VI Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering CLAIB 2014, Paraná, Argentina 29, 30 & 31 October 2014, Springer.
Li, A., C. Li, et al. (2013). Automated Segmentation of Prostate MR Images Using Prior Knowledge Enhanced Random Walker. Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), 2013 International Conference on, IEEE.
Qiu, W., J. Yuan, et al. (2014). Prostate segmentation: An efficient convex optimization approach with axial symmetry using 3-D TRUS and MR images. Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on 33(4): 947-960.
Xie, Q. and D. Ruan (2014). Low-complexity atlas-based prostate segmentation by combining global, regional, and local metrics. Medical physics 41(4): 041909.
Zhao, T. and D. Ruan (2015). Two-stage fusion set selection in multi-atlas-based image segmentation. Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2015 IEEE 12th International Symposium on, IEEE.
Collection: QIN Sarcoma
- Meyer JM, Perlewitz KS, Hayden JB, Doung Y-C, Hung AY, Vetto JT, Pommier RF, Mansoor A, Beckett BR, Tudorica A. Phase I trial of preoperative chemoradiation plus sorafenib for high-risk extremity soft tissue sarcomas with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI correlates. Clinical Cancer Research. 2013;19(24):6902-11.
Collection: REMBRANDT
Sereika, M., Urbanaviciute, R., Tamasauskas, A., Skiriute, D., & Vaitkiene, P. (2018). GFAP expression is influenced by astrocytoma grade and rs2070935 polymorphism. Journal of Cancer, 9(23), 4496-4502. DOI: 10.7150/jca.26769
Schrock, M. S. (2017). Wwox deficiency in human cancers: Role in treatment resistance. Columbus, OH: The Ohio State University. Retrieved from https://etd.ohiolink.edu/!etd.send_file?accession=osu1492793625915816&disposition=inline
Babu, B. S., & Varadarajan, S. (2017). Detection of brain tumour in MRI scan images using Tetrolet Transform and SVM classifier. Indian Journal of Science and Technology, 10. DOI:10.17485/ijst/2017/v10i19/113721
Collection: RIDER Collections
Arimura, H., Soufi, M., Ninomiya, K., Kamezawa, H., & Yamada, M. (2018). Potentials of radiomics for cancer diagnosis and treatment in comparison with computer-aided diagnosis. Radiological Physics and Technology, 48, 27-36. DOI: 10.1007/s12194-018-0486-x
Buch, K., Kuno, H., Qureshi, M. M., Li, B., & Sakai, O. (2018). Quantitative variations in texture analysis features dependent on MRI scanning parameters: A phantom model. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12482
- Barani R, Sumathi M. A New Adaptive-Weighted Fusion Rule for Wavelet based PET/CT Fusion. International Journal of Signal Processing, Image Processing and Pattern Recognition. 2016;9(11):271-82. DOI: 10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.11.25
- Aerts, H. J. W. L. et al. Defining a Radiomic Response Phenotype: A Pilot Study using targeted therapy in NSCLC. Sci. Rep.(2016) 6, 33860 (link)
Oliveira B, O'Halloran M, Conceicao R, Glavin M, Jones E. Development of Clinically-Informed 3D Tumor Models for Microwave Imaging Applications. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 2016;15:520-3. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2015.2456051
- Melouah A. Comparison of Automatic Seed Generation Methods for Breast Tumor Detection Using Region Growing Technique. Computer Science and Its Applications: Springer; 2015. p. 119-28.
- Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RTH, Parmar C, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nature Communications, 2014. 5(4006). DOI:10.1038/ncomms5006 (link)
- Balagurunathan Y, Kumar V, Gu Y, Kim J, Wang H, Liu Y, Goldgof DB, Hall LO, Korn R, Zhao B. Test–Retest Reproducibility Analysis of Lung CT Image Features. Journal of digital imaging. 2014:1-19.
Melouah, A. (2015). Comparison of Automatic Seed Generation Methods for Breast Tumor Detection Using Region Growing Technique. Computer Science and Its Applications, Springer: 119-128.
Desseroit M-C, Visvikis D, Tixier F, Majdoub M, Perdrisot R, Guillevin R, Le Rest CC, Hatt M. Development of a nomogram combining clinical staging with 18F-FDG PET/CT image features in non-small-cell lung cancer stage I–III. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. 2016:1-9. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-016-3325-5
These refer to the RIDER Collections data, created before submission to TCIA
- Meyer CR, Armato SG III, Fenimore CP, McLennan G, Bidaut LM, Barboriak DP, Gavrielides MA, Jackson EF, McNitt-Gray MF, Kinahan PE, Petrick N, Zhao B. Quantitative imaging to assess tumor response to therapy: Common themes of measurement, truth data and error sources. Translational Oncology 2: 198–210, 2009. (link)
- McNitt-Gray MF, Bidaut LM, Armato SG III, Meyer CR, Gavrielides MA, Fenimore CP, McLennan G, Petrick N, Zhao B, Reeves AP, Beichel R, Kim H-J, Kinnard L. CT assessment of response to therapy: Tumor volume change measurement, truth data and error.Translational Oncology2009. 2:216–222. (link)
- Kinahan PE, Doot RK, Wanner-Roybal M, Bidaut LM, Armato SG III, Meyer CR, McLennan G.PET/CT assessment of response to therapy: Tumor change measurement, truth data and error.Translational Oncology 2:223–230, 2009. (link)
- Jackson EF, Barboriak DP, Bidaut LM, Meyer CR. Magnetic resonance assessment of response to therapy: tumor change measurement, truth data and error sources.Translational Oncology 2009 Dec;2(4):211-5. PubMed PMID: 19956380; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2781079. (link)
- Armato SG 3rd, Meyer CR, Mcnitt-Gray MF, McLennan G, Reeves AP, Croft BY, Clarke LP;RIDER Research Group. The Reference Image Database to Evaluate Response to therapy in lung cancer (RIDER) project: a resource for the development of change-analysis software.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008 Oct;84(4):448-56. PubMed PMID: 18754000. (link)
Collection: Soft-tissue-Sarcoma
- Lee, I., Im, H.-J., Solaiyappan, M., & Cho, S. Y. (2017). Comparison of novel multi-level Otsu (MO-PET) and conventional PET segmentation methods for measuring FDG metabolic tumor volume in patients with soft tissue sarcoma. EJNMMI Physics, 4(22), 1-10. DOI 10.1186/s40658-017-0189-0
- Hermessi, H., Mourali, O., & Zagrouba, E. (2019). Deep feature learning for soft tissue sarcoma classification in MR images via transfer learning. Expert Systems with Applications, 120, 116-127. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.11.025
Collection: SPIE-AAPM Lung CT Challenge
- Park SY and Sargent D. Tumor propagation model using generalized hidden Markov model. Proc. SPIE 10133, Medical Imaging 2017: Image Processing, 101331G February 24, 2017); 10.1117/12.2254583
- Sargent D, Park S-Y. Semi-automatic 3D lung nodule segmentation in CT using dynamic programming. Proc. SPIE 10133, Medical Imaging 2017: Image Processing, 101332R (February 24, 2017) DOI: 10.1117/12.2254575
- Nishio M, Nagashima C. Computer-aided Diagnosis for Lung Cancer: Usefulness of Nodule Heterogeneity. Academic Radiology. 2017;24(3):328-36. (link)
Collection: SPIE-AAPM-NCI PROSTATEx Challenges
- A Chaddad, T Niazi, S Probst, F Bladou, M Anidjar, B Bahoric. (2018) Predicting Gleason Score of Prostate Cancer Patients using Radiomic Analysis. Frontiers in Oncology. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00630
Collection: TCGA-BRCA
Lehrer, M., Bhadra, A., Aithala, S., Ravikumar, V., Zheng, Y., Dogan, B., Bonaccio, E., Burnside, E. S., Morris, E., Sutton, E., Whitman, G. J., Net, J., Brandt, K., Ganott, M., Zuley, M., Rao, A., & TCGA Breast Phenotype Research Group. (2018). High-dimensional regression analysis links magnetic resonance imaging features and protein expression and signaling pathway alterations in breast invasive carcinoma. Oncoscience, 5(1-2), 39-48. (link)
Al-Dabagh MZ, AL-Mukhtar FH. Breast Cancer Diagnostic System Based on MR images Using KPCA-Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machine. IJAERS. 2017;4(3):258-63. DOI: 10.22161/ijaers.4.3.41
- Angela Giardino, Supriya Gupta, Emmi Olson, Karla Sepulveda, Leon Lenchik, Jana Ivanidze, Rebecca Rakow-Penner, Midhir J. Patel, Rathan M. Subramaniam, Dhakshinamoorthy Ganeshan. Role of Imaging in the Era of Precision Medicine. Academic Radiology, Available online 25 January 2017 DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.11.021
- Albiol, Alberto; Corbi, Alberto; Albiol, Francisco. Automatic intensity windowing of mammographic images based on a perceptual metric. Medical Physics, 2473-4209.10.1002/mp.12144
- Wu, J; Sun, X; Wang, J; Cui, Y; Kato, F; Shirato, H; Ikeda, DM.; Li, R. Identifying relations between imaging phenotypes and molecular subtypes of breast cancer: Model discovery and external validation. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2586 DOI: 10.1002/jmri.25661
Wu J, Cui Y, Sun X, Cao G, Li B, Ikeda DM, Kurian AW, Li R. Unsupervised clustering of quantitative image phenotypes reveals breast cancer subtypes with distinct prognoses and molecular pathways. Clinical Cancer Research. 2017:clincanres. 2415.016. (link)
- Mazurowski MA, Zhang J, Grimm LJ, Yoon SC, Silber JI. Radiogenomic Analysis of Breast Cancer: Luminal B Molecular Subtype Is Associated with Enhancement Dynamics at MR Imaging. Radiology, 2014. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14132641 (link)
Lavasani, S. N., A. F. Kazerooni, et al. (2015). Discrimination of Benign and Malignant Suspicious BreastTumors Based on Semi-Quantitative DCE-MRI ParametersEmploying Support Vector Machine. Frontiers in Biomedical Technologies 2(2): 397-403.
Anand, S., V. Vinod, et al. Application of Fuzzy c-means and Neural networks to categorize tumor affected breast MR Images. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 10(64): 2015.
Guo, W., H. Li, et al. (2015). Prediction of clinical phenotypes in invasive breast carcinomas from the integration of radiomics and genomics data. Journal of Medical Imaging 2(4): 041007-041007.
Kim, G. R., Ku, Y. J., Cho, S. G., Kim, S. J., & Min, B. S. (2017). Associations between gene expression profiles of invasive breast cancer and breast imaging reporting and data system MRI lexicon. Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research, 93(1), 18-26. DOI: 10.4174/astr.2017.93.1.18
Collection: TCGA-GBM
Han, L., & Kamdar, M. R. (2018). MRI to MGMT: Predicting methylation status in glioblastoma patients using convolutional recurrent neural networks. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, 23, 331-342. (link)
ParthaSarathi, M., & Ansari, M. A. (2017). Multimodal retrieval framework for brain volumes in 3D MR volumes. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 1-12. DOI:10.1007/s40846-017-0287-4
Liu, Y., Xu, X., Yin, L., Zhang, X., Li, L., & Lu, H. (2017). Relationship between glioblastoma heterogeneity and survival time: An MR imaging texture analysis. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 1-7. DOI:10.3174/ajnr.A5279.
Beig N, Patel J, Prasanna P, et al. Radiogenomic analysis of hypoxia pathway reveals computerized MRI descriptors predictive of overall survival in Glioblastoma. SPIE Medical Imaging; 2017; 10134:1-10. International Society for Optics and Photonics. DOI:10.1117/12.2255694
Lee, J.K., Wang, J., Sa, J.K., et al. Spatiotemporal genomic architecture informs precision oncology in glioblastoma. Nature Genetics.(2017) DOI: 10.1038/ng.3806
Cui Y, Ren S, Tha KK, Wu J, Shirato H, Li R. Volume of high-risk intratumoral subregions at multi-parametric MR imaging predicts overall survival and complements molecular analysis of glioblastoma. European Radiology. 2017:1-10. (link)
Kanas VG, Zacharaki EI, Thomas GA, Zinn PO, Megalooikonomou V, Colen RR. Learning MRI-based classification models for MGMT methylation status prediction in glioblastoma. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine. 2017;140:249-57.(link)
Czarnek N, Clark K, Peters KB, Mazurowski MA. Algorithmic three-dimensional analysis of tumor shape in MRI improves prognosis of survival in glioblastoma: a multi-institutional study. Journal of Neuro-Oncology. 2017:1-8. (link)
Chaddad A, Desrosiers C, Toews M, editors. Radiomic analysis of multi-contrast brain MRI for the prediction of survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2016 IEEE 38th Annual International Conference; 2016.
Prasanna, P., Patel, J., Partovi, S. et al. Radiomic features from the peritumoral brain parenchyma on treatment-naïve multi-parametric MR imaging predict long versus short-term survival in glioblastoma multiforme: Preliminary findings. Eur Radiol (2016) pp 1–10. DOI:10.1007/s00330-016-4637-3
Mulvey M, Muhyadeen S, Sinha U. Classification of Glioblastoma Multiforme Molecular Subtypes Using Three-Dimensional Multi-Modal MR Imaging Features. Med. Phys. 43, 3373 (2016); (link)
- Ren X, Cui Y, Gao H, Li, R. Identifying High-Risk Tumor Volume Based On Multi-Region and Integrated Analysis of Multi-Parametric MR Images for Prognostication of Glioblastoma. Med. Phys. 43, 3751 (2016); (link)
- Dunn WD Jr, Aerts HJWL, et al. Assessing the Effects of Software Platforms on Volumetric Segmentation of Glioblastoma. J Neuroimaging Psychiatry Neurol 2016. 1(2): 64-72.
- Upadhaya T, Morvan Y, et al. Prognosis classification in glioblastoma multiforme using multimodal MRI derived heterogeneity textural features: impact of pre-processing choices. Proc. SPIE 9785, Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 97850W (March 24, 2016); (link)
Upadhaya T, Morvan Y, et al. Prognostic value of multimodal MRI tumor features in Glioblastoma multiforme using textural features analysis. In Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2015 IEEE 12th International Symposium on, pp. 50-54. IEEE, 2015.
Upadhaya T, Morvan Y, et al. A framework for multimodal imaging-based prognostic model building: Preliminary study on multimodal MRI in Glioblastoma Multiforme. IRBM. 2015 Nov 30;36(6):345-50.
Reza SM, Mays R, Iftekharuddin KM, editors. Multi-fractal detrended texture feature for brain tumor classification. SPIE Medical Imaging; 2015: International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Nabizadeh N, Kubat M. Brain tumors detection and segmentation in MR images: Gabor wavelet vs. statistical features. Computers & Electrical Engineering. 2015.
Natteshan N, Jothi JAA. Automatic Classification of Brain MRI Images Using SVM and Neural Network Classifiers. Advances in Intelligent Informatics: Springer; 2015. p. 19-30. (link)
Zhang J, Barboriak DP, Hobbs H, Mazurowski MA. A fully automatic extraction of magnetic resonance image features in Glioblastoma patients. Medical physics. 2014;41(4):042301.
Wangaryattawanich P, Wang J, Thomas GA, Chaddad A, Zinn PO, Colen RR, editors. Survival analysis of pre-operative GBM patients by using quantitative image features. Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT), 2014 International Conference on; 2014: IEEE.
Colen RR, Wang J, Singh SK, Gutman DA, Zinn PO. Glioblastoma: Imaging Genomic Mapping Reveals Sex-specific Oncogenic Associations of Cell Death. Radiology. 2014.
- Colen RR, Vangel M, Wang J, Gutman DA, Hwang SN, Wintermark M, Rajan J, Jilwan-Nicola M, Chen JY, Raghavan P, Holder CA, Rubin D, Huang E, Kirby J, Freymann J, Jaffee CC, Flanders A, Zinn PO. Imaging genomic mapping of an invasive MRI phenotype predicts patient outcome and metabolic dysfunction: a TCGA glioma phenotype research group project.BMC Medical Genomics, 2014. 7(1):30. DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-7-30 (link)
- Gevaert O, Mitchell LA, Achrol AS, Xu J, Echegaray S, Steinberg GK, Chesier SH, Napel S, Zaharchuk G, Plevritis SK. Glioblastoma Multiforme: Exploratory Radiogenomic Analysis by Using Quantitative Image Features. Radiology, 2014. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14131731 (link)
- Mazurowski MA, Zhang J, Peters KB, and Hobbs H. Computer-extracted MR imaging features are associated with survival in glioblastoma patients. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 2014. 120(3):483–488 DOI: 10.1007/s11060-014-1580-5 (link)
- Jain R, Poisson L, Gutman D, Scarpace L, Hwang SN, Holder C, Wintermark M, Colen RR, Kirby J, Freymann J, Jaffe C, Mikkelsen T, Flanders A. Outcome Prediction in Patients with Glioblastoma by Using Imaging, Clinical, and Genomic Biomarkers: Focus on the Nonenhancing Component of the Tumor. Radiology. 2014 Aug;272(2):484-93. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14131691. Epub 2014 Mar 19. 2014 (link)
- Nicolasjilwan M, Hu Y, Yan C, Meerzaman D, Holder CA, Gutman D, et al. Addition of MR imaging features and genetic biomarkers strengthens glioblastoma survival prediction in TCGA patients. Journal of Neuroradiology, July 2014. DOI: 10.1016/j.neurad.2014.02.006
- Wassal E, Zinn P, Colen R. Diffusion and conventional MR imaging genomic biomarker signature for EGFR mutation identification in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology. 2014;16(suppl 5):v156-v7.
Wassal E, Zinn P, Colen R. Diffusion and conventional and MR imaging genomic biomarker signature predicts IDH-1 mutation in glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology. 2014;16(suppl 5):v157-v.
Kwon D, Shinohara RT, Akbari H, Davatzikos C. Combining Generative Models for Multifocal Glioma Segmentation and Registration. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2014: Springer; 2014. p. 763-70.
- Amer A, Zinn P, Colen R. Immediate post operative volume of abnormal flair signal predicts patient survival in glioblastoma patients. Neuro-Oncology. 2014;16(suppl 5):v138-v.
- Amer A, Zinn P, Colen R. Immediate post-resection pericavitarian DWI hyperintensity in glioblastoma patients is predictive of patient outcome. Neuro-Oncology. 2014;16(suppl 5):v138-v9.
- Gutman DA, Cooper LAD, Hwang SN, Holder CA, Gao J, Aurora TD, Dunn WD, Scarpace L, Mikkelsen T, Jain R, Wintermark M, Jilwan M, Raghavan P, Huang E, Clifford RJ, Monqkolwat P, Kleper V, Freymann J, Kirby J, Zinn PO, Moreno CS, Jaffe C, Colen R, Rubin DL, Saltz J, Flanders A, Brat DJ. MR Imaging Predictors of Molecular Profile and Survival: Multi-institutional Study of the TCGA Glioblastoma Data Set. Radiology. 2013 May:267(2):560-569,DOI:10.1148/radiol.13120118 (link)
- Jain R, Poisson L, Narang J, Gutman D, Scarpace L, Hwang SN, Holder C, Wintermark M, Colen RR, Kirby J, Freymann J, Brat DJ, Jaffe C, Mikkelsen T. Genomic Mapping and Survival Prediction in Glioblastoma: Molecular Subclassification Strengthened by Hemodynamic Imaging Biomarkers. Radiology, 2013 Apr:267(1):212 –220, DOI:10.1148/radiol.12120846 (link)
- Mazurowski MA, Desjardins A, Malof JM. Imaging descriptors improve the predictive power of survival models for glioblastoma patients. Neuro-oncology, 2013. 15(10):1389-1394 (link)
- Zinn PO, Colen RR. Imaging Genomic Mapping in Glioblastoma. Neurosurgery 60:126-130. Aug 2013 (link)
- Jain R, Poisson L, Narang J, Scarpace L, Rosenblum ML, Rempel S, Mikkelson T. Correlation of Perfusion Parameters with Genes Related to Angiogenesis Regulation in Glioblastoma: A Feasibility Study. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 2012. 33(7):1343-1348 [Epub ahead of print] (link)
- Zinn PO, Sathyan P, Mahajan B, Bruyere J, Hegi M, et al. A Novel Volume-Age-KPS (VAK) Glioblastoma Classification Identifies a Prognostic Cognate microRNA-Gene Signature. PLoS ONE, 2012 7(8): e41522. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0041522 (link)
- Zinn PO, Majadan B, Sathyan P, Singh SK, Majumder S, et al. Radiogenomic Mapping of Edema/Cellular Invasion MRI-Phenotypes in Glioblastoma Multiforme. PLoS ONE, 2011 6(10): e25451. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0025451 (link)
Wangaryattawanich, P., M. Hatami, et al. "Multicenter imaging outcomes study of The Cancer Genome Atlas glioblastoma patient cohort: imaging predictors of overall and progression-free survival." Neuro-oncology, (2015): nov117 .
Kuo, J. S., K. B. Pointer, et al. (2015). "139 Human Ether-a-Go-Go-Related-1 Gene (hERG) K+ Channel as a Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target for Glioblastoma." Neurosurgery 62: 210-211.
Zinn, P. O., M. Hatami, et al. (2015). "138 Diffusion MRI ADC Mapping of Glioblastoma Edema/Tumor Invasion and Associated Gene Signatures." Neurosurgery 62: 210.
Steed, T., J. Treiber, et al. (2015). "Iterative Probabilistic Voxel Labeling: Automated Segmentation for Analysis of The Cancer Imaging Archive Glioblastoma Images." American Journal of Neuroradiology 36(4): 678-685.
Lee, J., S. Narang, et al. (2015). "Associating spatial diversity features of radiologically defined tumor habitats with epidermal growth factor receptor driver status and 12-month survival in glioblastoma: methods and preliminary investigation." Journal of Medical Imaging 2(4): 041006-041006.
Itakura, H., A. S. Achrol, et al. (2015). "Magnetic resonance image features identify glioblastoma phenotypic subtypes with distinct molecular pathway activities." Science Translational Medicine 7(303): 303ra138-303ra138.
Cui, Y., K. K. Tha, et al. (2015). "Prognostic Imaging Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: Development and Independent Validation on the Basis of Multiregion and Quantitative Analysis of MR Images." Radiology: 150358.
Lee, J., S. Narang, et al. (2015). "Spatial Habitat Features Derived from Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data Are Associated with Molecular Subtype and 12-Month Survival Status in Glioblastoma Multiforme." PloS one 10(9): e0136557.
Rios Velazquez E, Meier R, Dunn WD Jr, Alexander B, Wiest R, Bauer S, Gutman DA, Reyes M, Aerts HJ. "Fully automatic GBM segmentation in the TCGA-GBM dataset: Prognosis and correlation with VASARI features." Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 18;5:16822. DOI: 10.1038/srep16822.
Collection: TCGA-KIRC
Nguyen, G. K., Mellnick, V. M., Yim, A. K.-Y., Salter, A., & Ippolito, J. E. (2018). Synergy of sex differences in visceral fat measured with CT and tumor metabolism helps predict overall survival in patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Radiology, 287(3), 884-892. DOI:10.1148/radiol.2018171504
Liu X, Swen JJ, Diekstra MHM, Boven E, Castellano D, Gelderblom H, Mathijssen RHJ, Vermeulen SH, Oosterwijk E, Junker K, Roessler M, Alexiusdottir K, Sverrisdottir A, Radu MT, Ambert V, Eisen T, Warren A, Rodriguez-Antona C, Garcia-Donas J, Bohringer S, Koudijs KKM, Kiemeney L, Rini BI, Guchelaar HJ. (2018) A genetic polymorphism in CTLA-4 is associated with overall survival in sunitinib-treated patients with clear cell metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2018. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2815
Chen X, Zhou Z, Thomas K, Wang J. Predicting Gene Mutations in Renal Cell Carcinoma Based On CT Imaging Features: Validation Using TCGA-TCIA Datasets. Med. Phys. 43, 3705 (2016); (link)- Zhu H, Chen H, Lin Z, Shi G, Lin X, Wu Z, Zhang X. Identifying molecular genetic features and oncogenic pathways of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through the anatomical (PADUA) scoring system. Oncotarget. 2016. (link)
- Shinagare AB, Vikram R, Jaffe C, Akin O, Kirby J, Huang E, Freymann J, Sainani NI, Sadow CA, Bathala TK. Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: preliminary findings of The Cancer Genome Atlas–Renal Cell Carcinoma (TCGA–RCC) Imaging Research Group. Abdominal imaging. 2015:1-9.
Collection: TCGA-LGG
- TA Juratli, SS Tummala, A Riedl, D Daubner, S Hennig, T Penson, A Zolal, C Thiede, G Schackert, D Krex, JJ Miller, DP Cahill. (2018) Radiographic assessment of contrast enhancement and T2/FLAIR mismatch sign in lower grade gliomas: correlation with molecular groups.Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 2018. DOI: 10.1007/s11060-018-03034-6
Halani, S. H., Yousefi, S.; Vega, J. V.; Rossi, M. R.; Zhao, Z.; Amrollahi, F.; Holder, C. A.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Eschbacher, J.; Griffith, B.; Olson, J. J.; Jiang, T.; Yates, J. R.; Eberhart, C. G.; Poisson, L. M.; Cooper, L. A. D.; Brat, D. J. (2018). Multi-faceted computational assessment of risk and progression in oligodendroglioma implicates NOTCH and PI3K pathways. Precision Oncology. DOI: 10.1038/s41698-018-0067-9
Liu, Z., Zhang, T., Jiang, H., Xu, W., & Zhang, J. (2018). Conventional MR-based preoperative nomograms for prediction of IDH/1p19q subtype in low-grade glioma. Academic Radiology. DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.09.022
Collection: TCGA-LUAD
Dara S, Tumma P, Eluri N, Kancharla G. Feature Extraction In Medical Images by Using Deep Learning Approach. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. 2018;120(6):305-12.
Pathak, Y., Arya, K. V., & Tiwari, S. (2018). An efficient low-dose CT reconstruction technique using partial derivatives based guided image filter. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 1-20. DOI: 10.1007/s11042-018-6840-5
Collection: TCGA-LUSC
- Walter, R., Rozynek, P., Casjens, S., Werner, R., Mairinger, F., Speel, E., Zur Hausen, A., Meier, S., Wohlschlaeger, J., Theegarten, D., Behrens, T., Schmid, K. W., Bruning, T., Johnen, G. (2018). Methylation of L1RE1, RARB, and RASSF1 function as possible biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of lung cancer. PLoS One, 13(5), e0195716. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0195716
Collection: 4D-Lung
- Woodruff, H. C., Shieh, C.-C., Hegi-Johnson, F., Keall, P. J. and Kipritidis, J. (2017), Quantifying the reproducibility of lung ventilation images between 4-Dimensional Cone Beam CT and 4-Dimensional CT. Med. Phys. DOI: 10.1002/mp.12199
- Hugo GD, Weiss E, Sleeman WC, Balik S, Keall PJ, Lu J, Williamson JF. A longitudinal four-dimensional computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography dataset for image-guided radiation therapy research in lung cancer. Med. Phys. (2017) DOI: 10.1002/mp.12059
1. Halani, S. H., Yousefi, S.; Vega, J. V.; Rossi, M. R.; Zhao, Z.; Amrollahi, F.; Holder, C. A.; Baxter-Stoltzfus, A.; Eschbacher, J.; Griffith, B.; Olson, J. J.; Jiang, T.; Yates, J. R.; Eberhart, C. G.; Poisson, L. M.; Cooper, L. A. D.; Brat, D. J. (2018). Multi-faceted computational assessment of risk and progression in oligodendroglioma implicates NOTCH and PI3K pathways. Precision Oncology.
10.1038/s41698-018-0067-9
1. Hermessi, H., Mourali, O., & Zagrouba, E. (2019, April 15). Deep feature learning for soft tissue sarcoma classification in MR images via transfer learning. Expert Systems with Applications, 120, 116-127.
10.1016/j.eswa.2018.11.025
https://urldefense.proofpoint.com/v2/url?u=http-3A__scholar.google.com_scholar-5Furl-3Furl-3Dhttps-3A__www.frontiersin.org_articles_10.3389_fonc.2018.00630_abstract-26hl-3Den-26sa-3DX-26d-3D17035574034759440838-26scisig-3DAAGBfm1WQblT5q86dJspvDOqRRu8PSVU7Q-26nossl-3D1-26oi-3Dscholaralrt-26hist-3DJZvdUd4AAAAJ-3A7503576860592939312-3AAAGBfm0I-5FIWDH8Wn1Tp7HZ80hnE7g7d1KA&d=DwMFaQ&c=27AKQ-AFTMvLXtgZ7shZqsfSXu-Fwzpqk4BoASshREk&r=XmScNBe7GWfThvx7zB1VFtrnLEkFz09aDyXm0X5WSKk&m=EheQAEDzYBdj1Hi3Mz5QJ6rjUvgeeGX13fmu6tj4P8I&s=I20gao5lOIC7cbYpu_7balkGSnBxbKOecD5UOqTXN44&e=